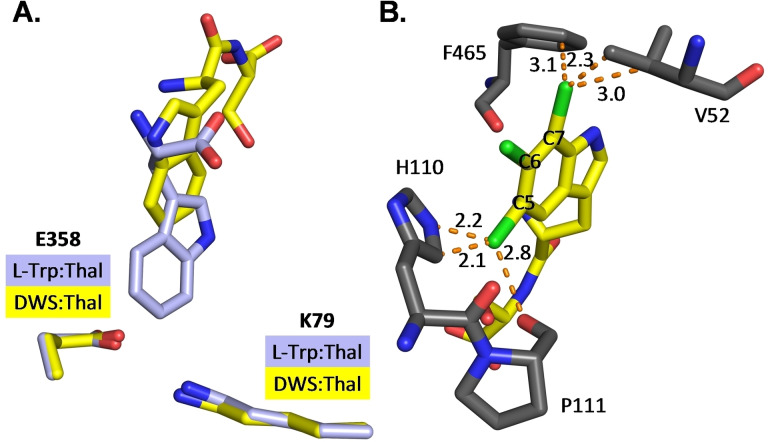
Figure 3.
(A) Orientation of d‐Trp‐Ser (DWS) in Thal. Superposition of bound d‐Trp‐Ser (yellow carbons; from PDB: 8AD8) and l‐Trp (light blue carbons, from PDB: 6H44) within the active site. The different position of the indole moiety leads to a longer distance between C6 and the ϵNH2 of the catalytic lysine. (B) Steric conflicts of potential chlorination positions. Replacement of the ligand d‐Trp‐Ser by its potential chlorination products leads to clashes (dotted orange lines, lengths in Å) of the chlorine (green) at position C5 and C7 with surrounding residues. Chlorination of the catalytically preferred C6 position does not cause clashes. d‐5‐Chloro‐Trp‐Ser, d‐6‐chloro‐Trp‐Ser and d‐7‐chloro‐Trp‐Ser were superimposed onto d‐Trp‐Ser (carbon atoms in yellow).