Figure 2.
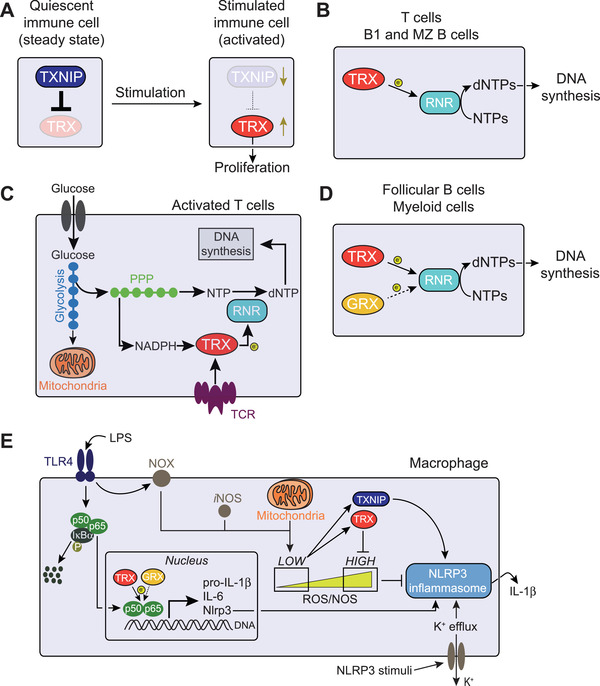
Immunoregulation by the TRX system. (A) Stimulated immune cells activate the thioredoxin (TRX) system by both increasing its transcriptional expression and by repressing its inhibitor thioredoxin‐interacting protein (TXNIP), thus promoting proliferation. (B) In T cells, B1, and marginal zone (MZ) B cells, the TRX system is the only pathway supporting ribonucleotide reductase (RNR)‐mediated reduction (electron [e−] donation) of ribonucleotides (NTPs) into the corresponding 2’‐deoxyribonucleotides (dNTPs) for DNA synthesis. (C) T cell stimulation reprogram cellular metabolism towards increased glycolysis and pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), which generates NADPH and building blocks for DNA synthesis. Concomitantly, upregulated TRX shuttles electrons from NADPH to RNR for dNTP production. (D) In follicular B cells and myeloid cells, both the TRX and the glutaredoxin (GRX) system can sustain DNA biosynthesis, although GRX‐dependent reaction is less efficient (dotted arrow). (E) TRX system‐dependent redox regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding to Toll‐like receptor 4 (TLR4) leads to phosphorylation (P) and consequent proteolysis of the NF‐κB inhibitor IκB‐α. This results in the release and translocation of NF‐κB p50 and p65 to the nucleus for transcription of genes encoding pro‐inflammatory cytokines (e.g. pro‐IL‐1β and IL‐6) and NLRP3 itself. TRX, and partially also GRX, positively regulates the binding of NF‐κB to target DNA, promoting transcriptional activity of target genes. NADPH oxidase (NOX) and mitochondrial metabolism generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), and nitric oxide (NO) synthase (iNOS) produces NO. Low ROS levels releases TRX from TXNIP‐mediated inhibition, which then leads to NLRP3 inflammasome activation and IL‐1β secretion. This is achieved by both TRX scavenging excessive ROS that would otherwise prevent inflammasome formation and by TXNIP potentially interacting with NLRP3 and enhancing IL‐1β production.
