FIG 1.
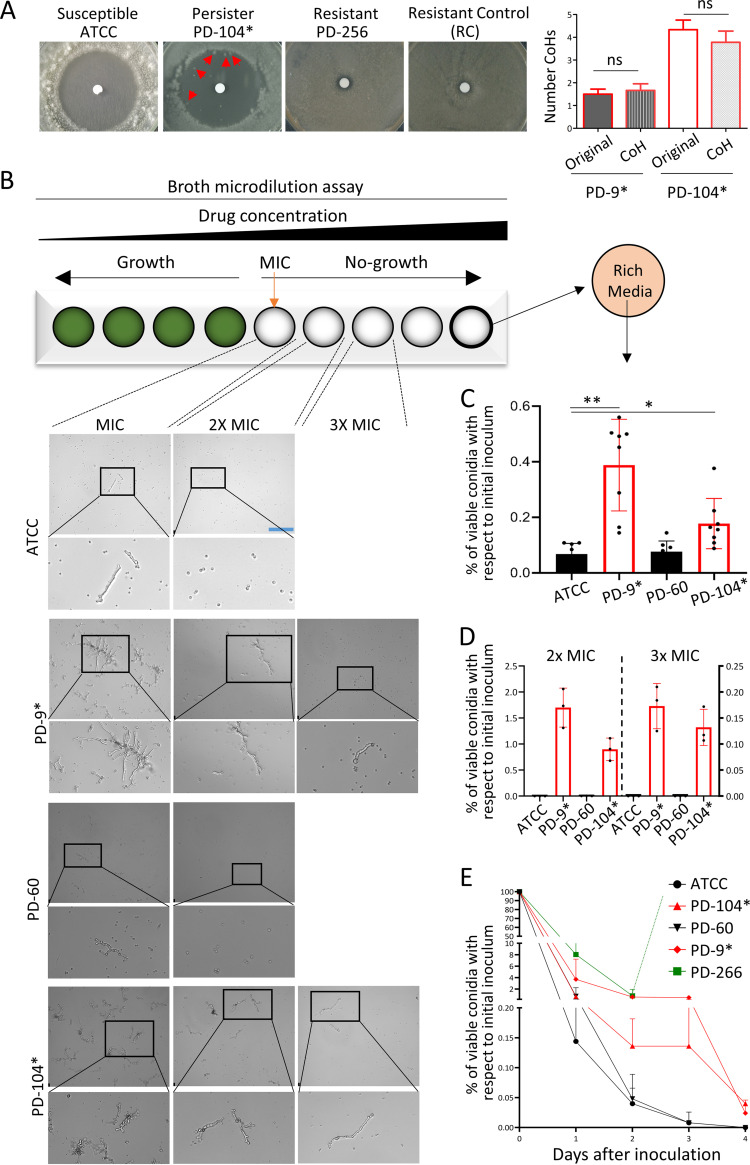
Certain A. fumigatus isolates display persistence to voriconazole. (A) In disc diffusion assays (10 μL of 0.8 mg/mL voriconazole), the susceptible isolate ATCC never grew any colony in the inhibition halo, and the resistant control (RC) isolate grew up to the edge of the disc, as did the strain PD-256. The persister isolate PD-104 was consistently able to grow a few small colonies. Plates were incubated for 5 days at 37°C. Quantification of the CoHs formed by persister isolates and their derived CoHs is shown. (B) Inspection of the wells of a broth dilution assay under a microscope 72 h after inoculation revealed that the nonpersister isolates ATCC and PD-60 displayed only limited microscopic growth at the MIC, and all conidia remained nongerminated at higher concentrations. In contrast, the persister strains PD-9 and PD-104 showed noticeable microscopic growth up to 3-fold (3×) the MIC. Scale bar, 132.5 μm. (C) The full content of the well containing the maximum concentration of voriconazole (8 μg/mL) was plated on rich medium PDA plates, and CFU were counted 48 h after inoculation. Persister isolates grew significantly more CFU than nonpersister isolates (PD-9 versus ATCC 46645C [P = 0.002] and PD-104 versus ATCC [P = 0.0331]), demonstrating that these strains remain viable upon azole treatment for a longer period. Three independent experiments with three biological replicates were performed. The graph represents the means and standard deviations (SD), and data were analyzed using the Brown-Forsythe and Welch analysis of variance (ANOVA) test with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons. (D) Conidia were directly inoculated on RPMI solid plates containing 2× or 3× the MIC of each isolate and incubated for 48 h at 37°C. The graph depicts the percentage of conidia from the original inoculum (2 × 104) that were able to form colonies. Three independent experiments were performed. (E) A survival curve in the presence of 4 μg/mL of voriconazole revealed that, while nonpersister strains lost viability very rapidly, the persister isolates had the characteristic biphasic reduction in viability, showing that a subpopulation of the persister isolates remained viable for a longer period. Two independent experiments with biological duplicates and two technical replicates were performed; the graph represents the means and SD. Persister isolates are labeled with an asterisk (*).