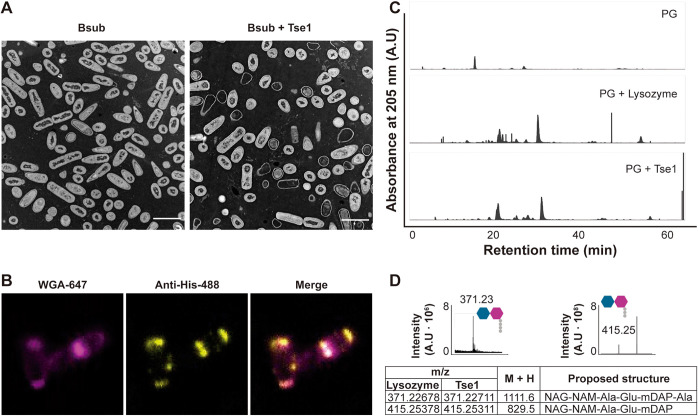
FIG 3.
Tse1 hydrolyzes Bacillus peptidoglycan. (A) Transmission electron micrograph of positively stained thin sections of Bacillus cells showing an overrepresentation of ghost cells after Tse1 treatment (Bsub + Tse1) compared with untreated cells (Bsub). After treatment with Tse1 (n = 85), 29.4% ghost cells were observed, compared to 0.95% ghost cells in untreated cells (n = 110) (n refers to the number of cells examined in each case). Bars, 2 μm. (B) Immunofluorescence assay of a Tse1-treated Bacillus bacterium immunolabeled with anti-His antibody conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488 (anti-His-488, yellow channel) and stained with WGA conjugated with Alexa Fluor 647 (WGA-647, pink channel). Protein accumulation is visible at the cell septa and poles. Images of untreated Bacillus cells and colocalization analysis are shown in an expanded view in Fig. 4A and B. (C) HPLC chromatograms of reduced soluble Bacillus peptidoglycan products obtained from digestion with lysozyme (PG + lysozyme, positive control), digestion with Tse1 (PG + Tse1), or treatment with buffer (PG [negative control]). (D) Partial HPLC chromatograms of muropeptides eluted at 55.89 min (371.23 m/z) and 63.65 min (415.25 m/z) obtained after Tse1 treatment. Peak assignments were made based on MS data and literature review. Predicted structures are shown with hexagons (NAM and NAG) and circles. The table shows the most abundant and relevant peaks found in samples treated with lysozyme or Tse1, their mass in daltons (M+H), and the proposed structures. NAG, N-acetylglucosamine; NAM, N-acetylmuramic acid; Ala, alanine; Glu, glutamic acid; mDAP, meso-diaminopimelic acid; A.U., arbitrary units. In all experiments, at least three biological replicates were obtained.