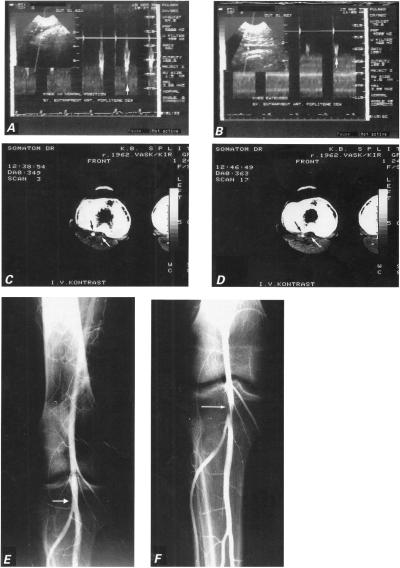
Fig. 1 Case 1: A) Doppler sonogram shows normal popliteal artery flow (vertical arrow) with knee in neutral position. B) Doppler tracing of popliteal artery flow with knee hyperextended during plantar extension of the foot shows monophasic configuration of the velocity waveform, with a blunt and rounded peak (vertical arrow) that suggests minor arterial stenosis. C) Computed tomographic scan performed after intravenous injection of contrast material shows enlarged medial head of gastrocnemius muscle joined with the accessory head (white arrow), and the normal lumen of the artery (black arrow). D) Computed tomographic scan with knee extended shows compression of artery (black arrow) by the accessory head of gastrocnemius muscle (white arrow). E) Arteriogram shows normal right popliteal artery (white arrow) with knee in the neutral position. F) Arteriogram of the hyperextended right knee shows constriction of the popliteal artery at the site of entrapment (white arrow).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.