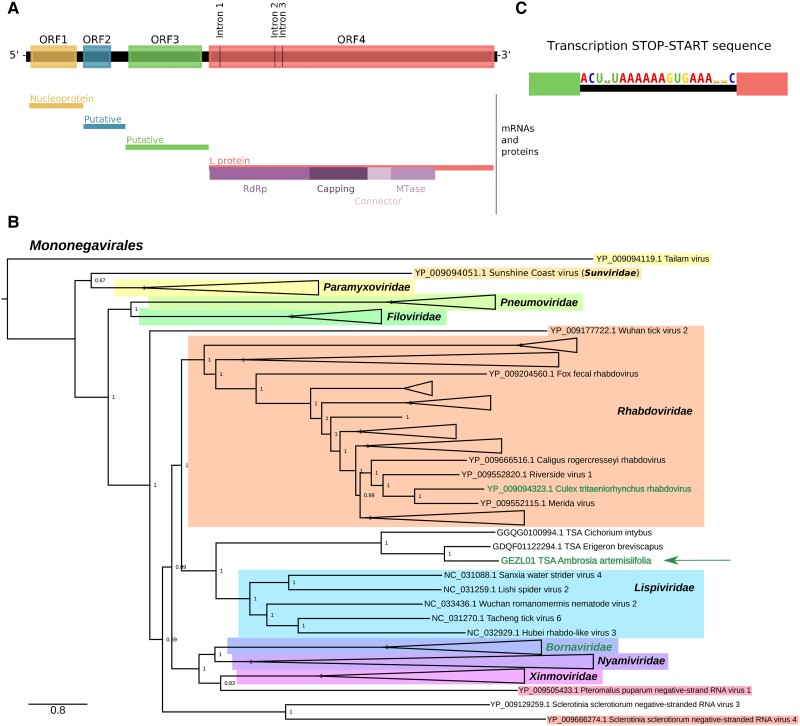
Fig. 8.
Splicing in a new rhabdo-like virus sequence. (A) Genome map of the rhabdo-like virus derived from the GEZL01 TSA data set. The diagram illustrates ORFs in the antigenome after removal of the identified introns. The positions of the removed introns are indicated. Putative transcription stop–start (TSS) sequences were identified between the ORFs, and the corresponding inferred mRNAs and their products (where identified) are indicated below as well as domains of the L protein. (B) Phylogenetic tree of Mononegavirales L protein sequences showing the placement of the GEZL01-derived rhabdo-like virus. For visual convenience, some clades are collapsed into isosceles triangles. Names of sequences/clades with known splicing are written in a different color (green; the GEZL01 sequence is marked with an arrow). See supplementary figure S14, Supplementary Material online for the complete tree. (C) Sequence logo generated from the three identified copies of the putative TSS sequence (shown in the antigenome sense), using CIAlign v 1.1.0 (Tumescheit et al. 2022).