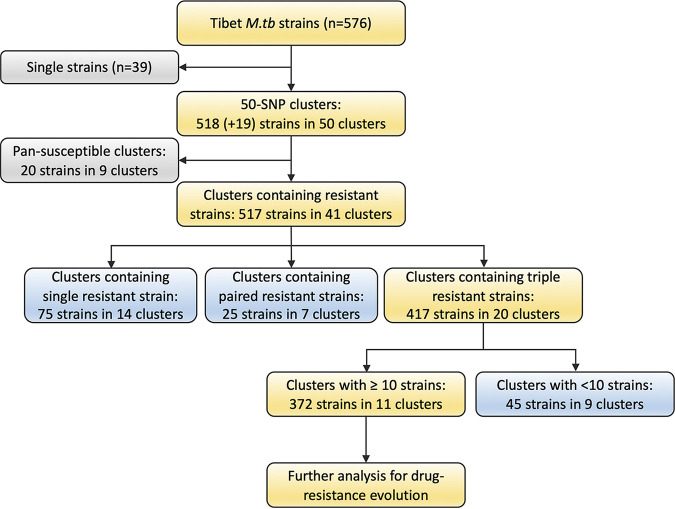
FIG 1.
Diagram of Tibetan M. tuberculosis strains included in the study. Using a pairwise distance of 50 SNPs, most strains (89.9%, 518/576) were phylogenetically separated into 50 long-term transmission clusters. Another 19 strains were embedded in the phylogenetic clusters, although they had longer genetic distances. Finally, 11 large clusters that contained consecutive ≥3 drug-resistant strains were included for evolution analysis. The clusters included 363 50-SNP clustered strains and another 9 phylogenetically embedded strains.