Abstract
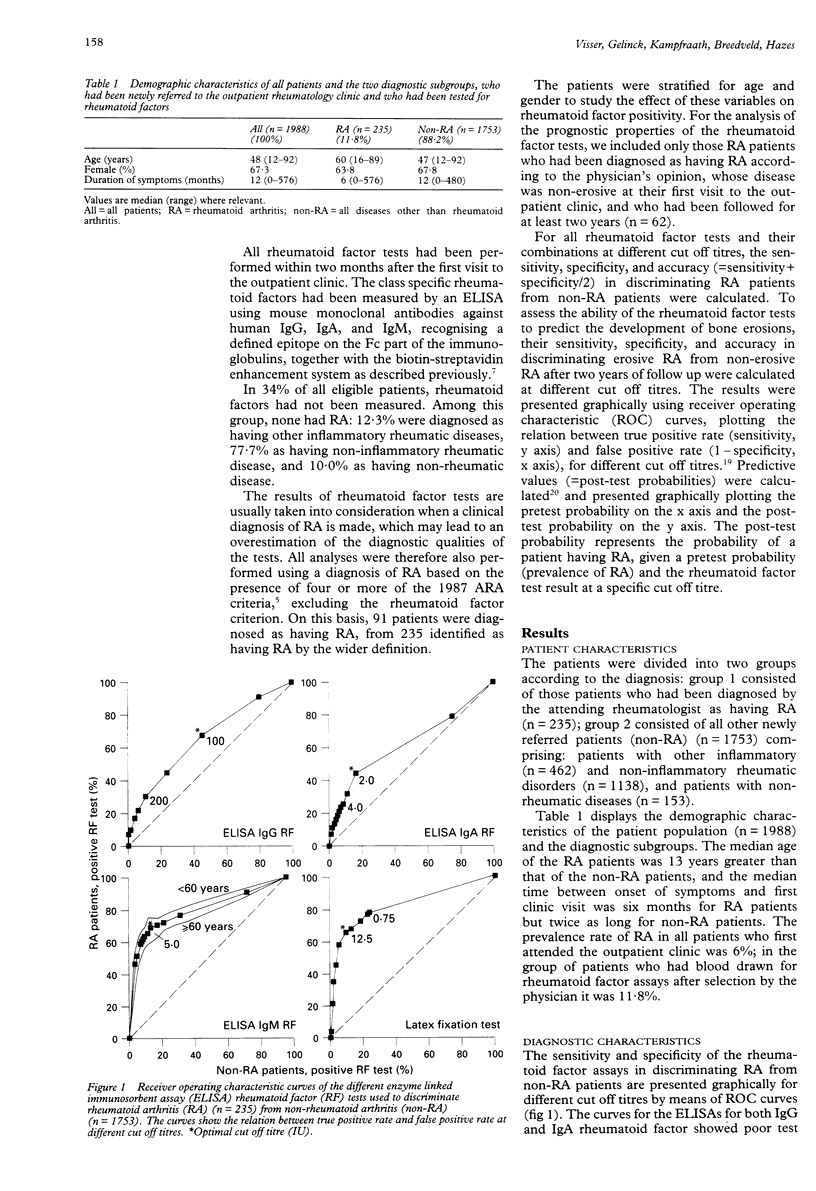
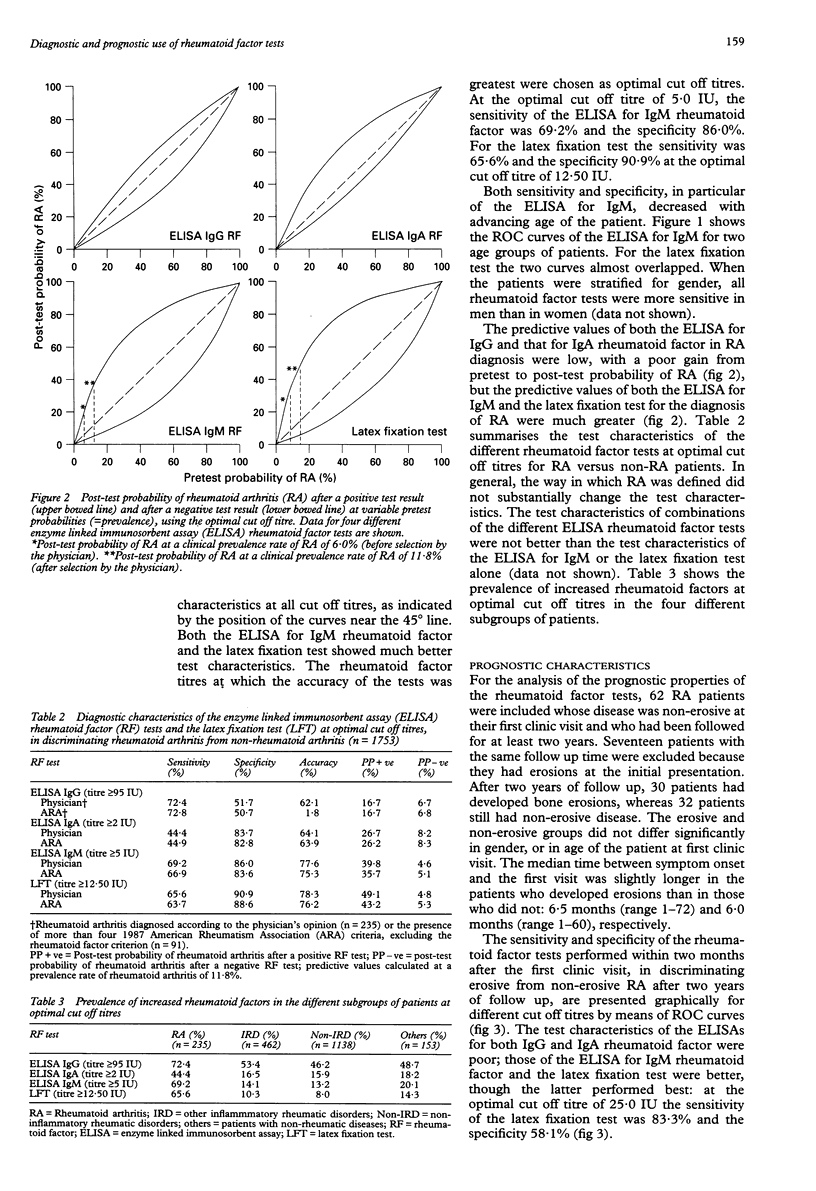
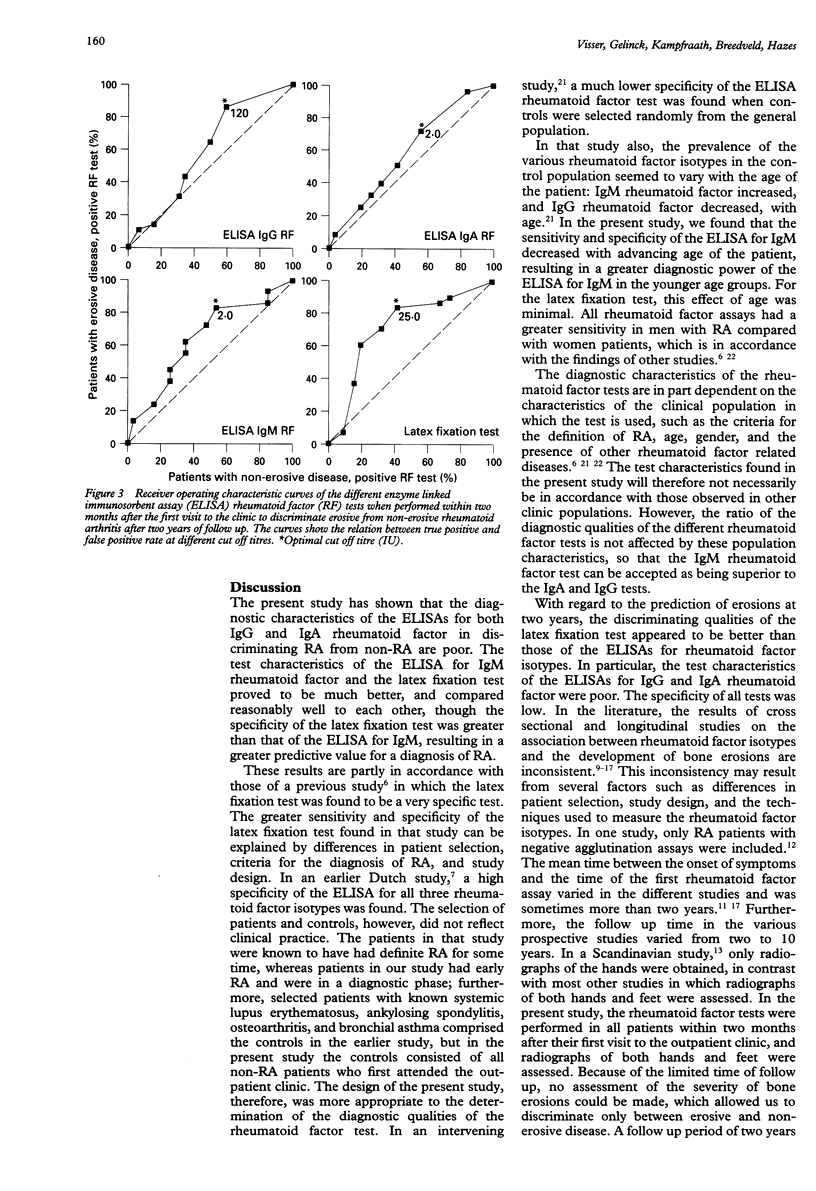
OBJECTIVE: To determine the diagnostic and prognostic test qualities of the enzyme linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) for rheumatoid factor isotypes in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and to compare them with the latex fixation test. METHODS: Rheumatoid factor tests were performed in 1988 consecutive new rheumatology outpatients within two months after their first visit to the outpatient clinic of the Department of Rheumatology of Leiden University hospital. The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and predictive values of the tests in discriminating RA from non-rheumatoid arthritis and erosive from non-erosive disease after two years of follow up were determined and presented as receiver operating characteristic curves and post-test probability curves. RESULTS: The sensitivity of the ELISA for IgG, IgA, and IgM rheumatoid factor for RA versus all controls at optimal cut off titres was 72%, 44%, and 69%, respectively; the specificity was 52%, 84%, and 86%. For the latex fixation test the sensitivity was 66% and the specificity 91%. The post-test probability of RA, at a clinical prevalence rate of 12%, given a positive test result in the ELISAs for IgG, IgA, and IgM rheumatoid factor and the latex fixation test, was 17%, 27%, 40%, and 49%, respectively; with negative test results the probability was 7%, 8%, 5%, and 5%, respectively. The specificity of all tests in discriminating erosive from non-erosive RA at two years was low: 41%, 44%, 47%, and 58% for the ELISAs for IgG, IgA, and IgM rheumatoid factor and the latex fixation test, respectively. CONCLUSION: The ELISAs for IgG and IgA rheumatoid factor are of no significance in diagnosing RA and in the prediction of erosive disease. The ELISA for IgM rheumatoid factor is a reasonable alternative for the latex fixation test when age and gender are taken in to consideration. The specificity of all rheumatoid factor tests in discriminating erosive from non-erosive RA is low.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aho K., Palosuo T., Raunio V., Puska P., Aromaa A., Salonen J. T. When does rheumatoid disease start? Arthritis Rheum. 1985 May;28(5):485–489. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aho K., Tuomi T., Heliövaara M., Palosuo T. Rheumatoid factors and rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1988;74:41–44. doi: 10.3109/03009748809102938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnason J. A., Jónsson T., Brekkan A., Sigurjónsson K., Valdimarsson H. Relation between bone erosions and rheumatoid factor isotypes. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 May;46(5):380–384. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.5.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook A., Corbett M. Radiographic changes in early rheumatoid disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Feb;36(1):71–73. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cats A., Klein F. Quantitative aspects of the latex-fixation and Whaaler-Rose tests. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 Nov;29(6):663–672. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.6.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhardt K. B., Svensson B., Truedsson L., Wollheim F. A. The occurrence of rheumatoid factor isotypes in early definite rheumatoid arthritis--no relationship with erosions or disease activity. J Rheumatol. 1988 Jul;15(7):1070–1074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egeland T., Munthe E. The role of the laboratory in rheumatology. Rheumatoid factors. Clin Rheum Dis. 1983 Apr;9(1):135–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggelmeijer F., Otten H. G., de Rooy H. H., Daha M. R., Breedveld F. C. Significance of rheumatoid factor isotypes in seronegative rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 1990;10(1):43–46. doi: 10.1007/BF02274780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gioud-Paquet M., Auvinet M., Raffin T., Girard P., Bouvier M., Lejeune E., Monier J. C. IgM rheumatoid factor (RF), IgA RF, IgE RF, and IgG RF detected by ELISA in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Jan;46(1):65–71. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jónsson T., Valdimarsson H. Is measurement of rheumatoid factor isotypes clinically useful? Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Feb;52(2):161–164. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten H. G., Daha M. R., de Rooij H. H., Breedveld F. C. Quantitative detection of class-specific rheumatoid factors using mouse monoclonal antibodies and the biotin/streptavidin enhancement system. Br J Rheumatol. 1989 Aug;28(4):310–316. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/28.4.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paimela L. The radiographic criterion in the 1987 revised criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Reassessment in a prospective study of early disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Mar;35(3):255–258. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkowski A., Nilsson L. A. Isotype-specific measurement of rheumatoid factor with reference to clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1983 Nov;12(3):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitsson I., Withrington R. H., Seifert M. H., Valdimarsson H. Prospective study of early rheumatoid arthritis. I. Prognostic value of IgA rheumatoid factor. Ann Rheum Dis. 1984 Oct;43(5):673–678. doi: 10.1136/ard.43.5.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valkenburg H. A., Ball J., Burch T. A., Bennett P. H., Lawrence J. S. Rheumatoid factors in a rural population. Ann Rheum Dis. 1966 Nov;25(6):497–508. doi: 10.1136/ard.25.6.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winska Wiloch H., Thompson K., Young A., Corbett M., Shipley M., Hay F. IgA and IgM rheumatoid factors as markers of later erosive changes in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1988;75:238–243. doi: 10.3109/03009748809096770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe F., Cathey M. A., Roberts F. K. The latex test revisited. Rheumatoid factor testing in 8,287 rheumatic disease patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Aug;34(8):951–960. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeben D., Hazes J. M., Zwinderman A. H., Cats A., van der Voort E. A., Breedveld F. C. Clinical significance of rheumatoid factors in early rheumatoid arthritis: results of a follow up study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Sep;51(9):1029–1035. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.9.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


