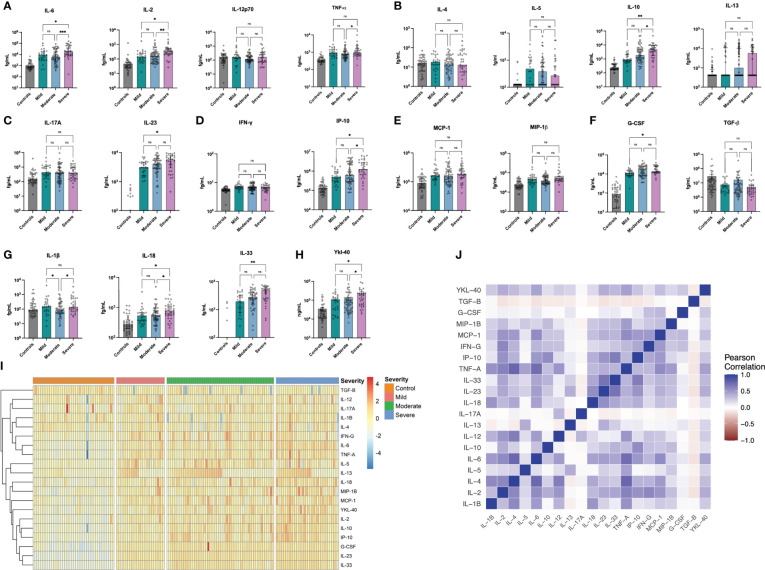
Figure 1.
Cytokine Concentrations in Acute COVID-19. IL-1β, IL-4, IL-5 and IL12p70 were not significantly elevated in acute COVID-19 patients whilst all other cytokines were significantly elevated (TGF-B was significantly lower in acute COVID-19). Eleven Markers, namely IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-10, IL-18, IL-23, IL-33, TNF-α, IP-10, G-CSF and YKL-40 all differed significantly by COVID-19 Severity. Data are presented for controls (n = 44) and those with mild (n = 26), moderate (n = 58) and severe (n = 44) COVID-19 for NF-kB-dependent IL-6 & Th1 cytokines (A), Th2 cytokines (B), Th17 cytokines (C), interferon-related proteins (D), chemokines (E), growth factors (F), IL-1 family cytokines (G) and Ykl-40 (H). Results are presented for A-H in femtograms/mL (fg/mL) on a logarithmic scale. Results are also presented as a heatmap of log-transformed, z-scored concentrations based on disease severity for the entire cohort (I) and as a correlation matrix (J) demonstrating the relationships between differing markers. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ns, non-significant. Strongest correlations were seen (R>0.7) between 6 pairs: IL-1β & IL-4, IL-1β & TNF-α, IL-1β & IL-6, between IL-6 & TNF-α; between TNF-α and IL-10 and between IP-10 & IL-33 which all persisted following Bonferonni correction.