Figure 6.
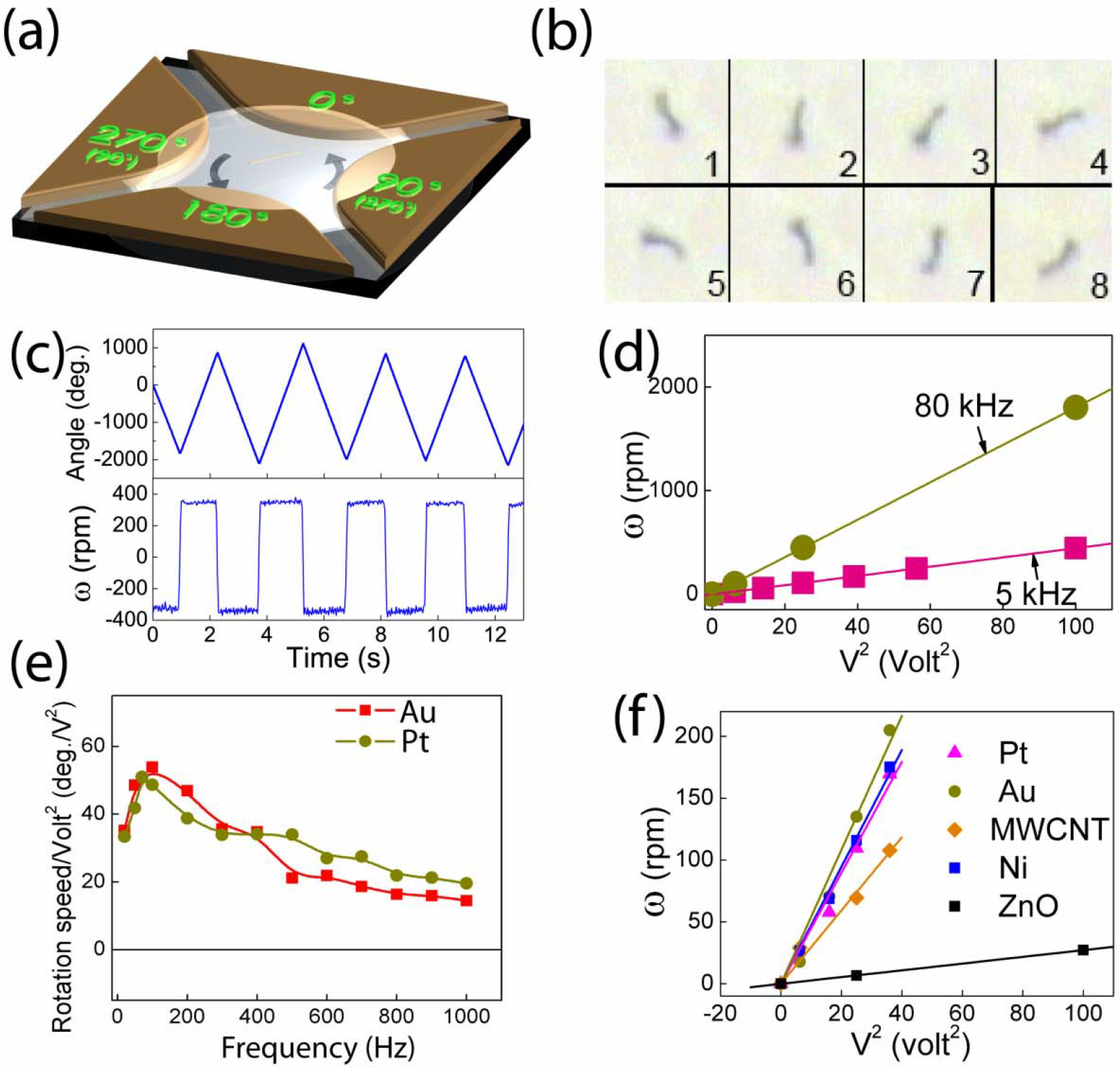
(a) Schematics of rotation of nanowires in suspension by AC voltages applied on the four parts with 900 phase shifts of a quadrupole electrode. (b) Overlapped images at 1/30 sec interval of free rotating Au nanowires (50 nm in diameter, 10 μm in length) at 5V, 20 kHz. (c) Angle and speed of rotation of Au nanowires at 4, 0, 6, 0, and −8 V. The start and stop of the rotation of the nanowires is instantaneous without apparent acceleration or deceleration. (d) Rotation speed of free Au nanowires at 5 and 80 kHz as a function of V 2. (e) Rotation speed normalized by V2 versus AC frequency at for free Au and Pt nanowires. (f) Rotation speed of Au, Ni, Pt nanowires (10 μm in length, 0.15 μm in radius), ZnO nanowires (5 μm in length, 0.2 μm in radius), and multiwall carbon nanotubes (5 μm in length, 10 nm in radius) versus V2.
