Figure 9.
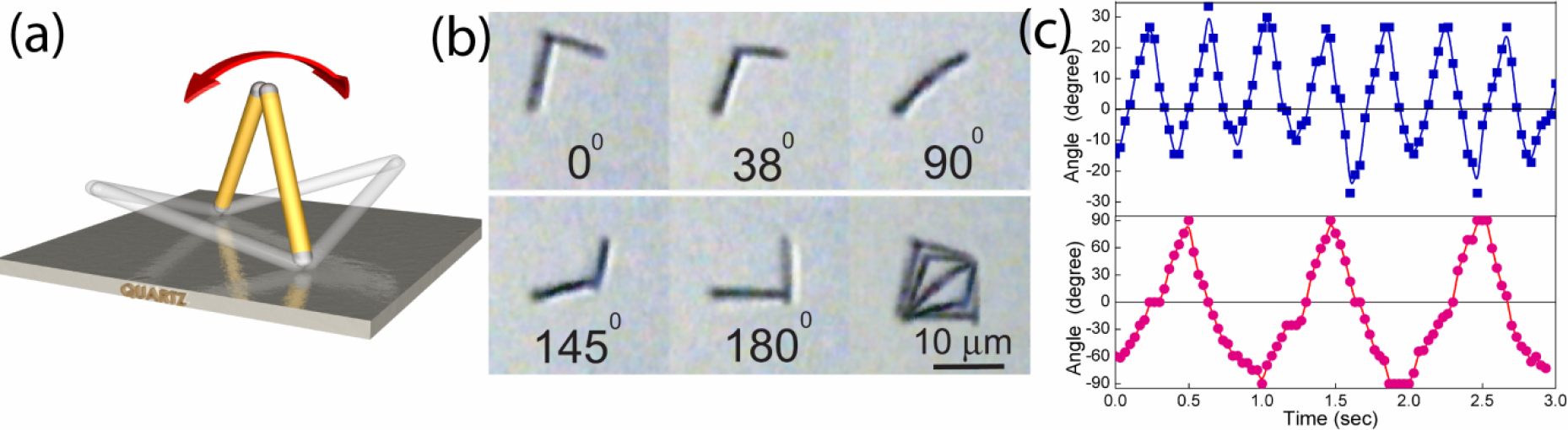
(a) Schematics of a nanowire oscillator assembled in D.I. water by joining two oppositely charged Au nanowires (6 μm), the joint secured by the magnetic Ni segments at the ends. (b) Top view images of the nanowire oscillator as it oscillates between 90° and −90°, the angle between the plane of the oscillator and the normal direction of the quartz substrate. The last picture shows the overlapped images. (c) The oscillation angle as a function of time showing the oscillation frequencies are same as that of the square wave E field at 1 kHz (blue line) and 2 kHz (pink line). We have controlled the frequency of the nano-oscillator from 0.5 to 2.5 Hz.
