Figure 3.
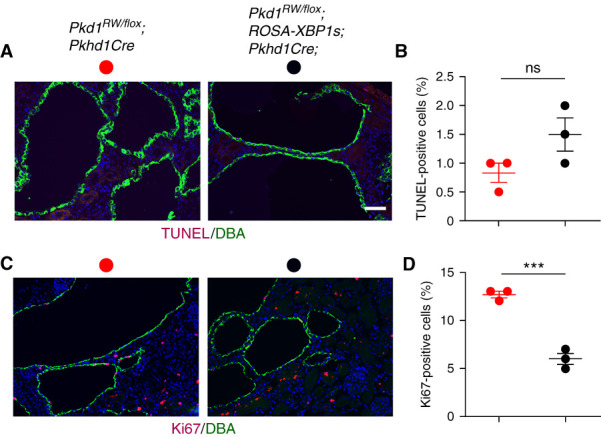
The in vivo effect of XBP1s occurs via a decrease in cell proliferation. Expression of XBP1s in the cystic epithelia of Pkd1R2216W/flox;Pkhd1Cre mice at P16 leads to a significant reduction of proliferation with no impact on apoptosis. (A) Representative images of TUNEL staining (apoptosis; red) in DBA-positive collecting duct segments (green) of Pkd1R2216W/flox;Pkhd1Cre and Pkd1R2216W/flox;ROSA-XBP1s;Pkhd1Cre mice. Sections were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) Quantitation of apoptosis for the genotypes described in (A). (C) Representative images of Ki67 staining (proliferation; red) in DBA-positive collecting duct segments (green) of Pkd1R2216W/flox;Pkhd1Cre and Pkd1R2216W/flox;ROSA-XBP1s;Pkhd1Cre mice. Sections were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 20 μm. (D) Quantification of proliferation indexes for genotypes described in (C). Apoptosis and proliferation rates were determined by counting >1000 DBA-positive collecting duct cells per kidney from three kidneys per each genotype for both TUNEL and Ki67. Results are shown as the mean±SEM (t test); n.s. P=0.09; ***P<0.001.
