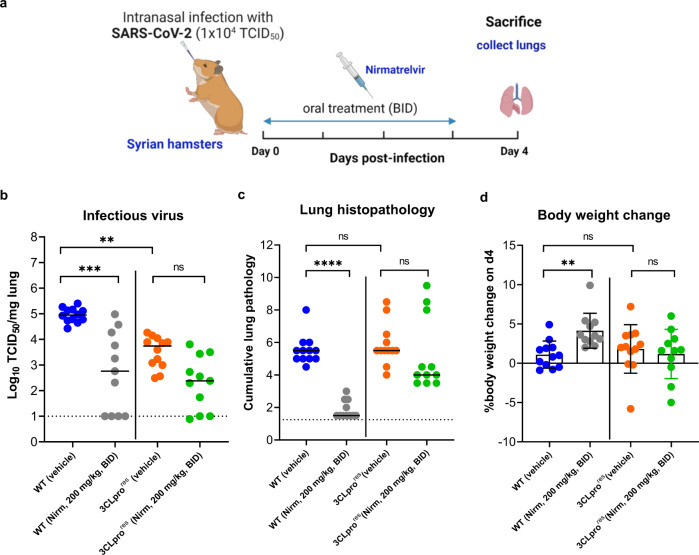
Fig. 3. In vivo efficacy of nirmatrelvir against the 3CLpro (L50F-E166A-L167F) resistant virus.
a Set-up of the study. b Infectious viral loads in the lungs of hamsters that were treated with vehicle or nirmatrelvir (Nirm) at 200 mg/kg (BID) and infected with 104 TCID50 of either the wild-type (WT) SARS-CoV-2 isolate (USA-WA1/2020) or the 3CLpro (L50F-E166A-L167F) nirmatrelvir resistant (3CLprores) virus at day 4 post-infection (pi) are expressed as log10 TCID50 per mg lung tissue. Individual data and median values are presented. c Cumulative severity score at day 4 p.i. from H&E stained slides of lungs from hamsters treated with either vehicle or nirmatrelvir (Nirm) and infected with either the WT SARS-CoV-2 isolate or 3CLprores virus. Individual data and median values are presented; the dotted line represents the median score of untreated non-infected hamsters. d Weight change at day 4 pi in percentage, normalized to the body weight at the time of infection. Bars represent means ± SD. Data were analyzed with the Kruskal–Wallis test, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns = non-significant. Data presented are from 2-independent studies with a total n = 12 per vehicle-treated groups and n = 11 for the nirmatrelvir-treated groups. Panel (a) designed by Biorender.