FIGURE 2.
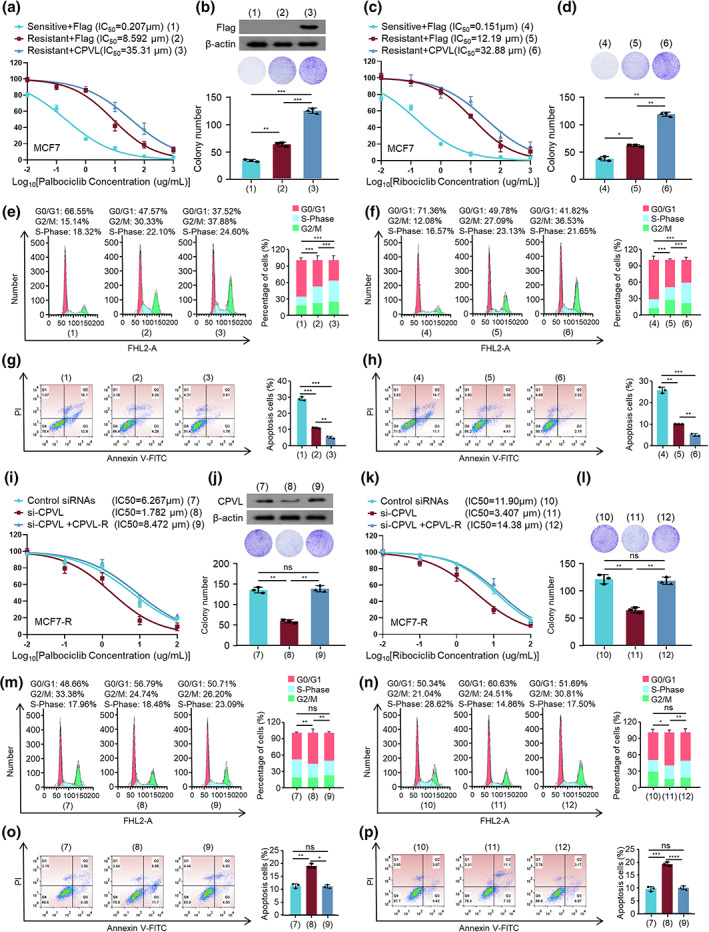
Resistance of breast cancer cells to CDK4/6 inhibitors was regulated by CPVL in vitro. Viability of MCF7‐S and MCF7‐R cells transfected with empty vector or Flag‐CPVL and incubated with gradient concentrations of palbociclib (a) or ribociclib (c). Colony formation of transfected cells incubated with 10 μM palbociclib (b) or 15 μM ribociclib (d). Cells were transfected with empty vector or Flag‐CPVL and incubated with gradient concentrations of palbociclib or ribociclib, then cell cycle distribution (e) and apoptosis (f) were evaluated by flow cytometry and ratios (%) of cells in G0/G1, S, or G2/M phases (g) and of apoptotic cells (h) were statistically analyzed. Cell viability assays of MCF7‐S and MCF7‐R cells transfected with control siRNAs or si‐CPVL or si‐CPVL plus CPVL‐R and incubated with gradient concentrations of palbociclib (i) or ribociclib (k). (j) Colony formation of cells with control siRNAs or si‐CPVL or si‐CPVL plus CPVL‐R and incubated with 10 μM palbociclib (J) or 15 μM ribociclib (l). Cells were transfected with control siRNAs or si‐CPVL or si‐CPVL plus CPVL‐R and incubated with gradient concentrations of palbociclib or ribociclib, then cell cycle distribution (m) and apoptosis (n) were evaluated by flow cytometry and ratios (%) of cells in G0/G1 or S or G2/M phases (o) and of apoptotic cells (p) were analyzed. All values are shown as mean ± SD of three sets of duplicates. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 vs. control
