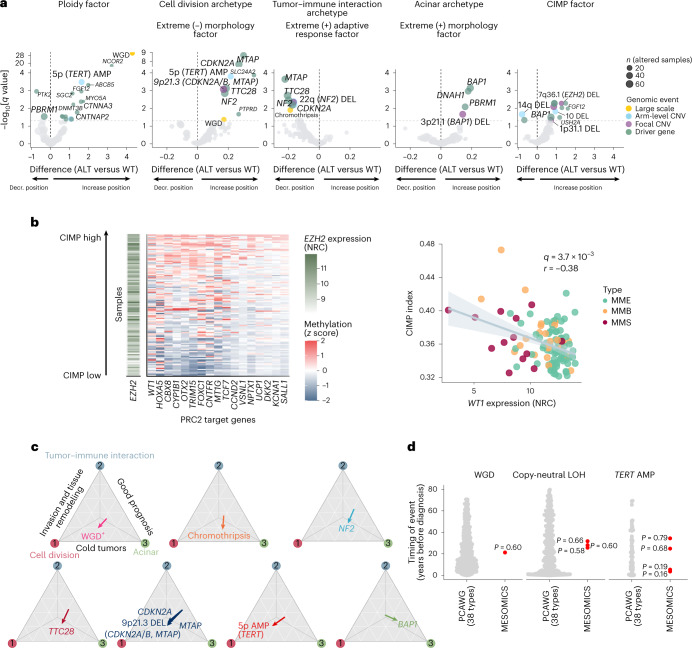
Fig. 5. Impact of genomic events on MPM molecular profiles.
a, Association between genomic events and MOFA factors. For each event, the ALT (altered) versus wild-type difference corresponds to the difference between the mean factor value of wild-type samples and that of altered samples. The q values correspond to an adjusted analysis of variance P value; the dashed horizontal line represents the q value threshold of 0.05. AMP, amplification; Decr., decrease; DEL, deletion. b, Association between CIMP index, EZH2 expression (n = 109 samples) and PRC2 target gene methylation (n = 119 samples). Left, heatmap of EZH2 gene expression (NRC) and CpG island methylation (z score) of PRC2 target genes whose methylation level was significantly positively correlated with CIMP index (q < 0.05), for samples ordered by CIMP index. Right: correlation between WT1 expression and CIMP index. The q value was determined by Pearson correlation test and the gray band corresponds to the 95% confidence interval. c, Effect vector of key alterations affecting specialization in the tumor tasks from Fig. 2. The effect vector corresponds to the difference in position on the Pareto front between the centroid of altered samples and the centroid of wild-type samples. d, Comparison of the timing of large-scale amplifications in the MESOMICS and PCAWG cohorts. The points represent estimates of the timing of genomic events. The empirical P values (red data points) were determined by one-sided outlier tests.