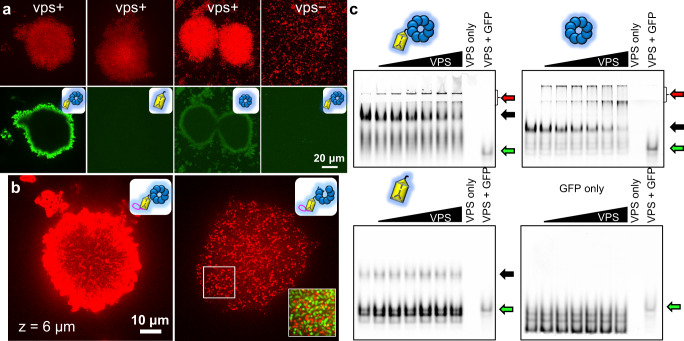
Fig. 2. A conserved β-propeller domain anchors Bap1 and RbmC to VPS.
a V. cholerae biofilms expressing mScarlet-I (Top) incubated with 1 μM purified and GFP-tagged proteins (Bottom) with the indicated domain(s). The VPS− control was performed with ΔvpsL cells unable to produce VPS. b Cross-sectional images (at z = 6 μm) of biofilms from cells expressing wild-type Bap1 (Left) and Bap1ΔVelcro (Right), both tagged with a 3×FLAG tag at the C-terminus and stained with an anti-FLAG antibody conjugated to Cy3. Inset: magnified image of the region highlighted by the white box, with the cell signal (mNeonGreen) overlaid with Cy3. c EMSA images showing the binding of purified Bap1’s β-propeller to purified VPS. Red arrows = protein-VPS complex, black arrows = unbound proteins, green arrows = free GFP. See Supplementary Fig. 2i for positive control and results from RbmC’s β-propeller. When present, the protein amount in a lane is 5 µg. The VPS amount is 0, 0.0625, 0.125, 0.25, 0.50, 1, 5, 5, 5 µg in each lane from left to right.