FIGURE 2.
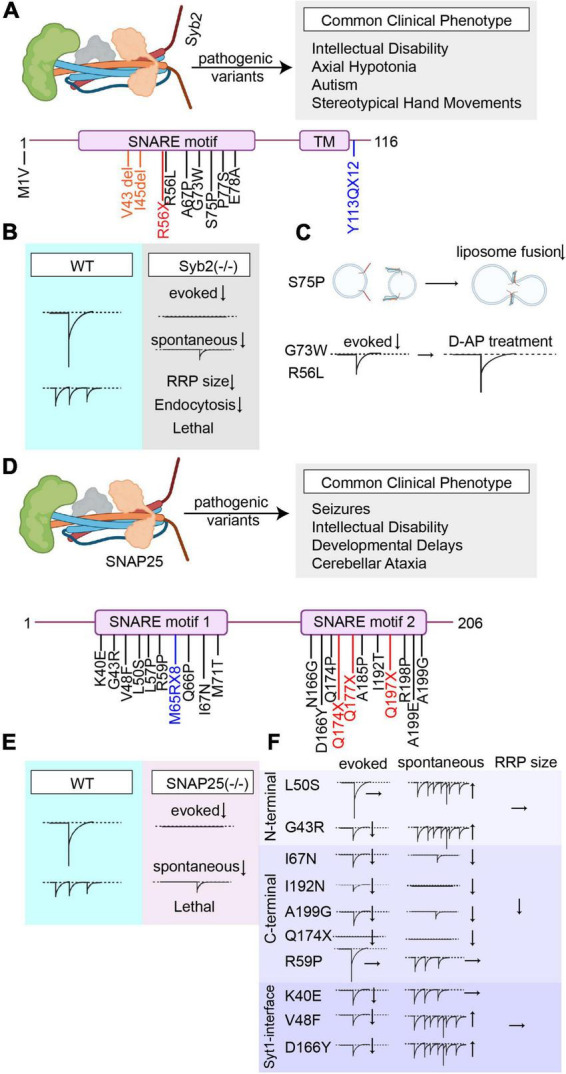
Overview of the pathogenic Syb2 and SNAP25 variants’ effects on synaptic vesicle release. (A) Summary of all reported pathogenic Syb2 (NCBI Accession #: AAF15551.1) variants and the most common clinical phenotype of the patients harboring these variants (Variants are color-coded based on their effects on the protein. Nonsense mutations are presented in red, missense mutations are presented in black, frameshift mutations are presented in blue, and deletions/insertions are presented in orange). (B) Graphical depiction demonstrating the changes in synaptic vesicle release upon genetic deletion of Syb2. (C) Graphical summary of the findings explaining aberrant forms of vesicle fusion and neurotransmission caused by different Syb2 variants (S75P, G73W, and R56L). (D) Summary of all reported pathogenic SNAP25 (NCBI Accession #: NP_001309838.1) variants and the most common clinical phenotype of the patients harboring these variants (Variants are color-coded based on their effects on the protein. Nonsense mutations are presented in red, missense mutations are presented in black, and frameshift mutations are presented in blue). (E) Graphical depiction demonstrating the changes in synaptic vesicle release upon genetic deletion of SNAP25. (F) Graphical summary of the findings explaining the effects of different SNAP25 variants (N-terminal, C-terminal, or Syt1-interface variants) on different modes of neurotransmitter release.
