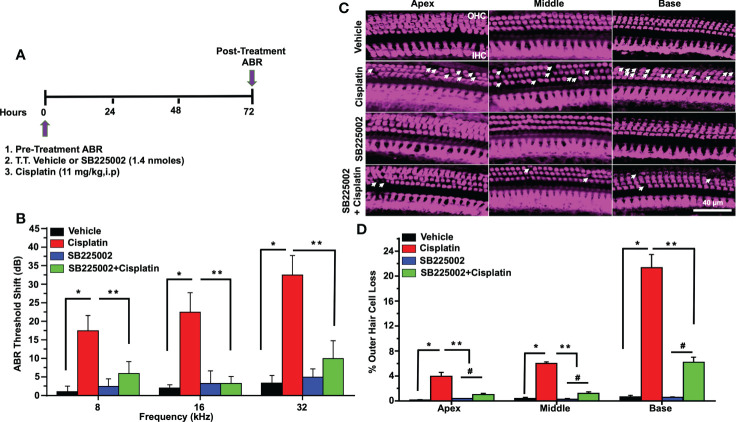
Figure 6.
Trans-tympanic delivery of SB225002 attenuated cisplatin-induced hearing loss. (A) Figure depicts experimental procedure that describes the dosage and route of administration for SB225002 (1.4 nmoles/ear) and cisplatin (11mg/kg). (B) ABR thresholds were recorded in Wistar rats which were then treated trans-tympanically with vehicle or SB225002 in both ears. Rats were then administered with vehicle or cisplatin (11 mg/kg) and ABRs were recorded 72 h later. Cisplatin produced a significant increase in ABR thresholds at 8,16 and 32 KHz frequencies which were attenuated by SB225002 at all frequencies tested. Data represent mean ± SEM of four rats (P<0.0001 between vehicle, cisplatin and SB225002+cisplatin, F(3,62)=19.89 and DF=62). (C) Cochleae were isolated, decalcified for 21 days with 120 mM EDTA (daily changed) and used for preparing whole mounts. Basal, middle and apex turns were stained with Myosin VIIa (magenta) to visualize OHCs and IHCs. Representative whole-mount images showed significant OHCs damage (white arrow) by cisplatin, while trans-tympanic pretreatment with SB225002 protected OHCs. Scale bar represent 20 µm. (D) Percentage missing OHCs in basal, middle and apex turns of cochlea were significantly decreased by pretreatment with SB225002 compared with cisplatin treated group. No loss of hair cells was observed in the vehicle or SB225002-treated cochleae (P<0.0001 between vehicle cisplatin and SB225002+cisplatin, F(3,12)=71.13 and DF=15) Data indicates mean ± SEM. Asterisks, (*) indicates significant difference from vehicle group, while (**) indicate significant difference form cisplatin group (n=4), (#) Indicate statistically significant difference from the cisplatin-treated group and from vehicle group. Statistical analyses among groups were tested using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).