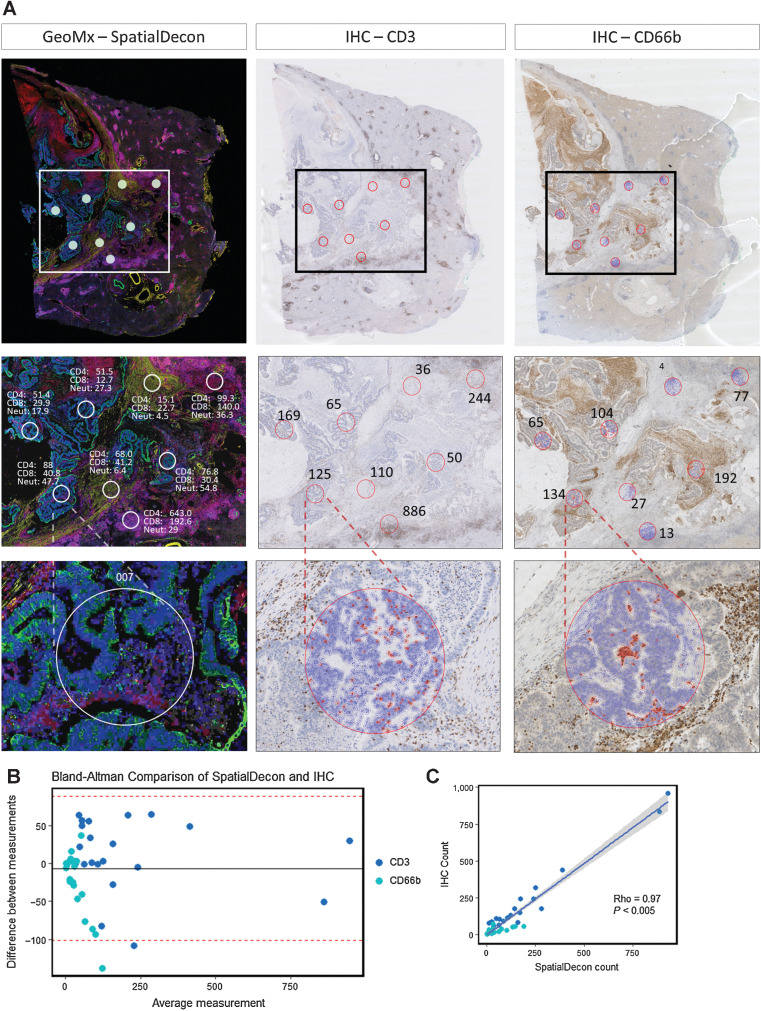
Figure 5.
Immune cell spatial deconvolution. A, Representative images from 1 CRLM (Patient A, Fig. 4A) showing cell detection from the Qupath package used on a CD3 and CD66b IHC-stained liver metastasis to count number of CD3 and CD66b-positive cells from 21 regions from a total of three CRLM. This count was compared with the SpatialDecon-derived count that uses the transcriptomic data from the corresponding ROI in the GeoMx mIF-stained matched sample (See Supplementary Fig. S5). B, Bland Altman plot comparing transcriptome SpatialDecon-derived cell count versus the IHC-derived cell count. C, Correlation plot comparing transcriptome SpatialDecon-derived cell count versus the IHC-derived cell count.