Fig. 1.
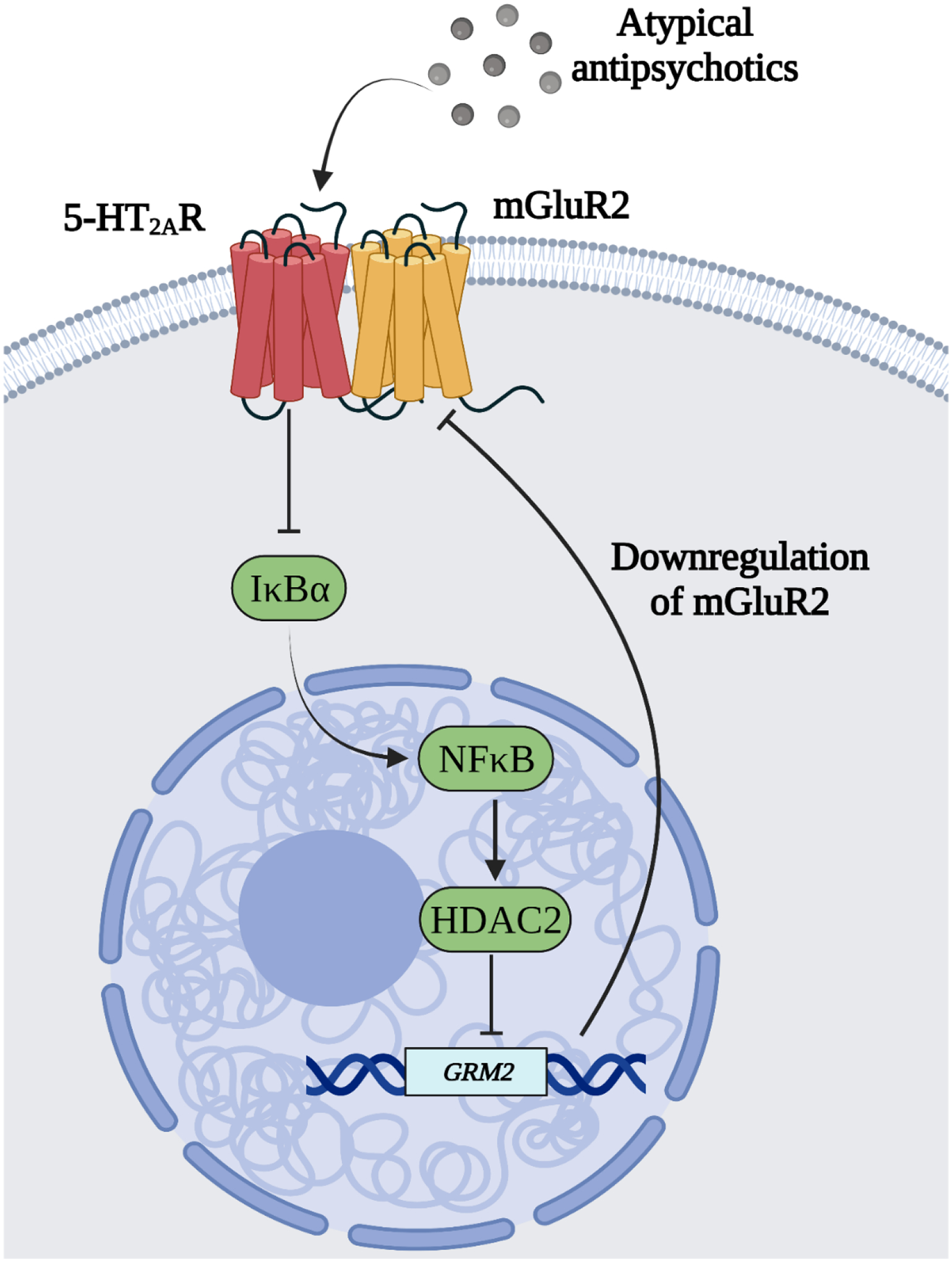
HDAC2-dependent regulation of mGluR2 transcription upon chronic atypical antipsychotic treatment. Chronic atypical antipsychotic treatment decreases density of 5-HT2AR in the frontal cortex, which also leads to down-regulation of the NF-κB repressor IκBα. This pathway induces NF-κB-dependent augmentation of HDAC2 expression and, consequently, increased binding of HDAC2 to the mGluR2 promoter. Together, these findings suggest that disinhibition of the NF-κB pathway by chronic treatment with atypical, but not typical, antipsychotics induces HDAC2-dependent repressive histone modifications at the mGluR2 promoter, which consequently restricts the antipsychotic effects of mGluR2/3 agonists.
