Figure 1.
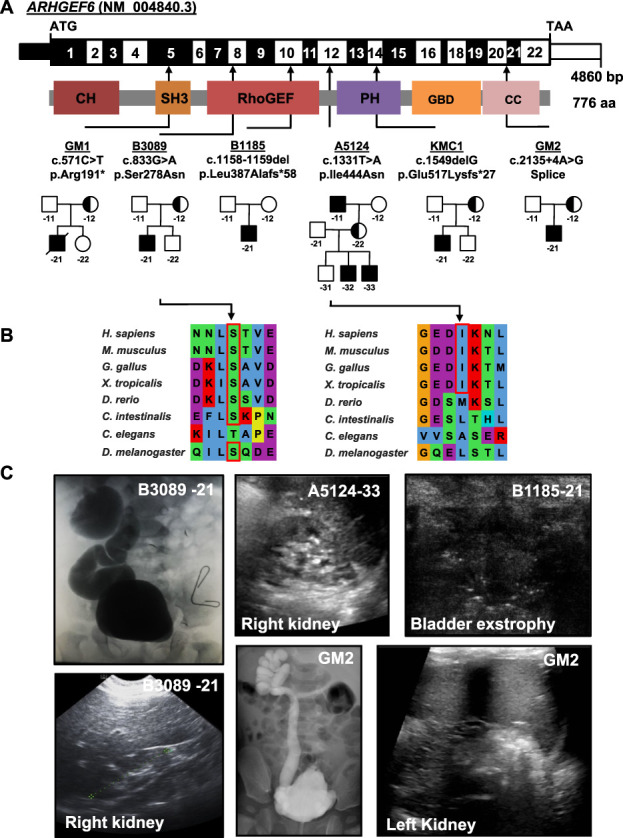
Exome sequencing identifies X-linked recessive variants in the gene ARHGEF6 in six families with CAKUT. (A) Exon structure (upper bar) and protein domains (lower bar) of human ARHGEF6. Positions of start codon (ATG) and stop codon (TAA) are indicated. Exon numbers are marked on an alternating black or white background. Protein domain lengths are shown by the colored boxes in respect to encoding exons. Positions of variants are indicated by black arrows in relation to the exon and the protein domain (see also Table 1). Pedigrees of families with genetic variants in ARHGEF6 are depicted below each family number. (B) CLUSTAL-generated amino acid sequence alignments of ARHGEF6 orthologous proteins are shown for the regions surrounding sites of missense variants. (C) Representative clinical images of individuals with ARHGEF6 variants. Upper row (from left to right): Voiding cysto-urethrogram showing vesico-uretral reflux grade IV or V on the right (B3089-21), renal ultrasound image of proband A5124-33 showing renal hypoplasia, and bladder ultrasound images of B1185-21 indicating bladder exstrophy. Lower row (from left to right): Renal ultrasound of right kidney (B3089-21) showing renal hypoplasia on the right. Voiding cysto-urethrogram showing vesico-uretral reflux grade V on the right (GM2) and renal ultrasound of left kidney of GM2 indicating hypoplastic kidney.
