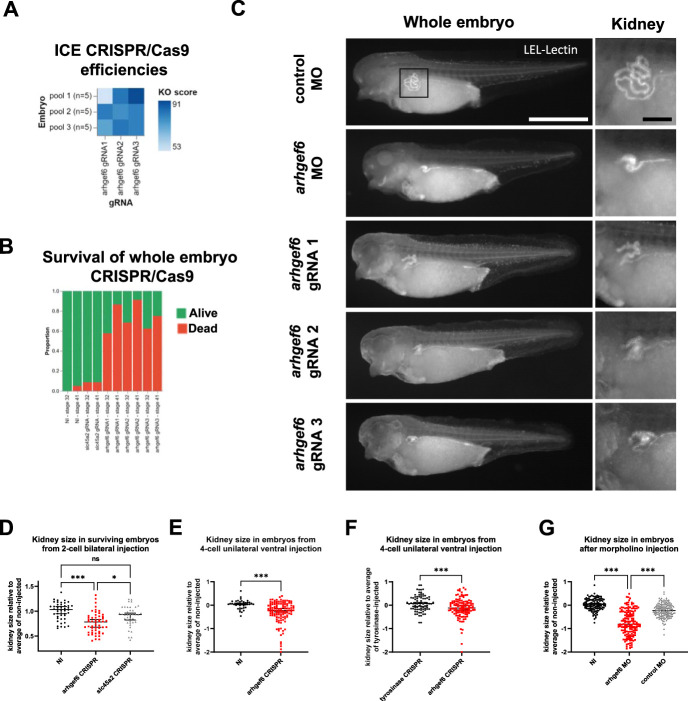
Figure 5.
Knockdown or knockout of arhgef6 impairs renal development in Xenopus larvae. (A) Three distinct gRNAs targeting arhgef6 were separately and bilaterally injected in both blastomeres of two-cell X. tropicalis embryos. Embryos were then lysed one day postfertilization, and CRISPR/Cas9 editing efficiencies were determined using Sanger sequencing and ICE deconvolution analysis. This demonstrated in vivo arhgef6 gene editing at high efficiency (86%±10%), enriched toward frameshift variants, yielding high knockout score (78%±10%) for all three gRNAs. (B) Bar graph shows relative frequency of effect on survival from global knockout of arhgef6 compared to noninjected embryos or embryos injected with slc45a2 gRNA, leading to albinism in the frog. (C) Fluorophore-conjugated lectin (LEL) was then used to stain proximal nephron parts to qualitatively compare kidney development in Xenopus embryos from different injections. Exemplary images are shown for arhgef6 gRNA, arghef6 morpholino, and control morpholino injections. LEL, Lycopersicon esculentum Lectin. White scale bar, 100 µm; black scale bar, 20 µm. (D) Scatter plot shows quantification of kidney size from two-cell stage bilateral injections, comparing noninjected, arghef6 gRNA and control slc45a2 gRNA-injected animals. Kruskal–Wallis test; NI, noninjected animal; *P<0.05; ***P<0.001. (E) Side comparison of kidney size from arghef6 gRNA unilateral four-cell stage ventral injection is shown. NI, noninjected side of same animal; Mann–Whitney test; ***P<0.001. (F) Side comparison of kidney size from arghef6 gRNA and tyrosinase gRNA in unilateral four-cell stage ventral injection is shown. Mann–Whitney test; ***P<0.001. (G) Scatter plot shows comparison of kidney size from morpholino-mediated knockdown of arghef6 using unilateral four-cell stage ventral injections using the following conditions: noninjected, arghef6 morpholino, control morpholino. Kruskal–Wallis test; NI, noninjected side; MO, morpholino; ***P<0.001.