Figure 3. Duplex backbone distortions facilitate formation of non-canonical base pairs.
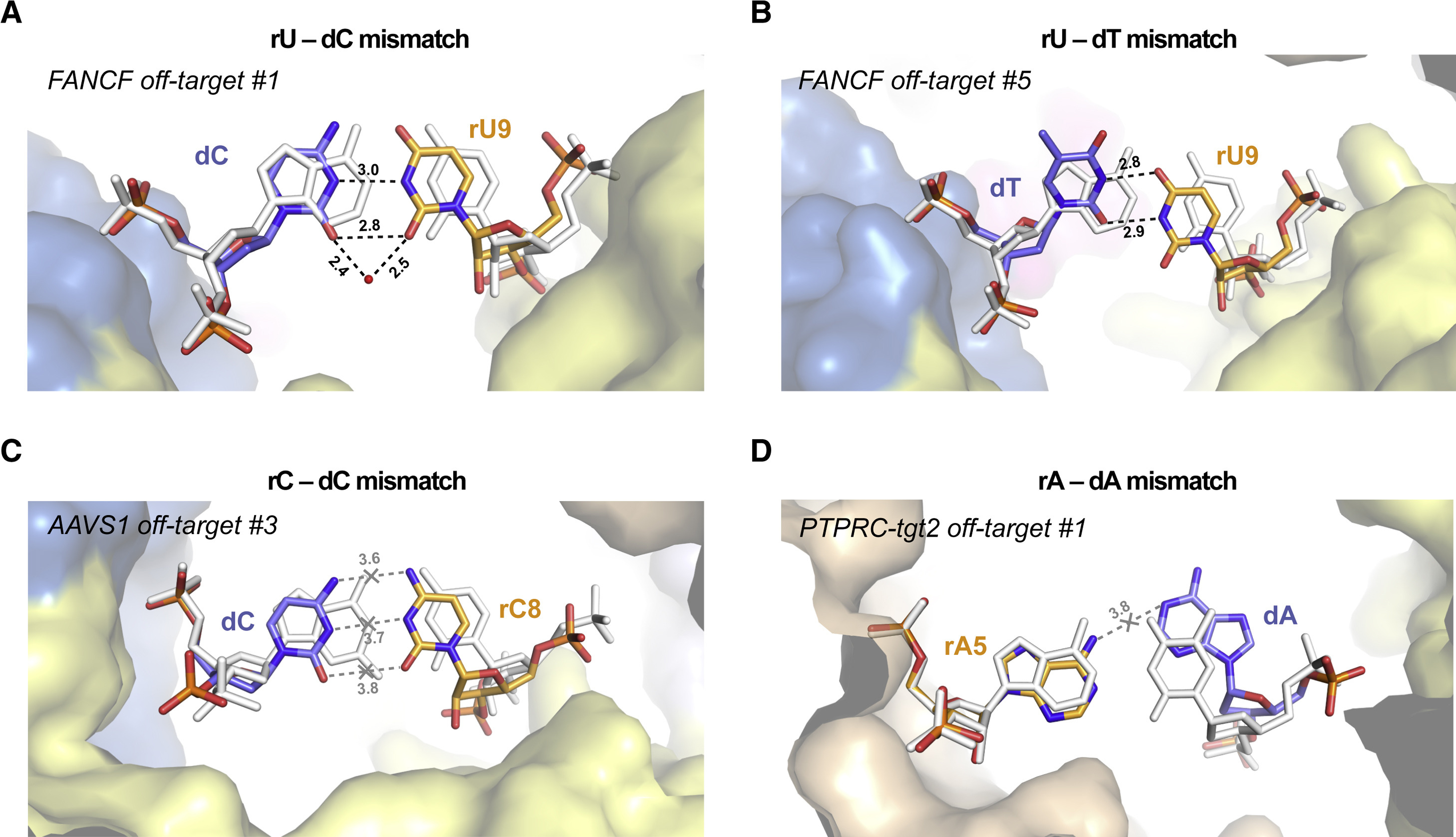
(A) Close-up view of the rU-dC base pair at duplex position 9 in FANCF off-target #1 complex, facilitated by lateral displacement of the guide RNA backbone. (B) Zoomed-in view of the rU-dT base pair at position 9 in FANCF off-target #5 complex. (C) Zoomed-in view of the rC-dC mismatch at duplex position 8 in AAVS1 off-target #3 complex. The distances between the cytosine bases indicate lack of hydrogen bonding. (D) Zoomed-in view of the rA-dA mismatch at duplex position 5 in PTPRC-tgt2 off-target #1 complex. Hydrogen bonding interactions are indicated with dashed lines. Corresponding on-target Watson-Crick base pairs are shown in white (for PTPRC-tgt2, the FANCF on-target structure was used and bases were mutated in silico). Numbers indicate interatomic distances in Å. Bound water molecule is depicted as red sphere. See also Figures S10, S11, S12, S13.
