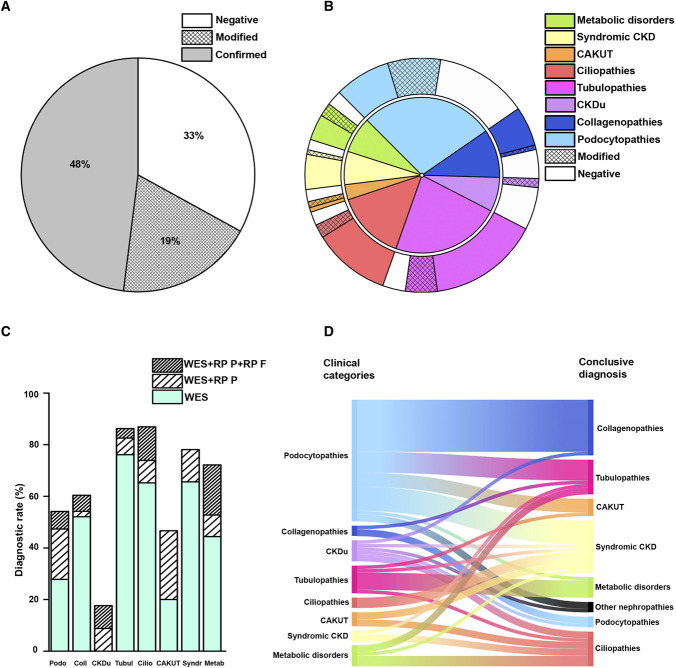
Figure 2.
Diagnostic rate and disease reclassification. (A) Percentage of diagnosis confirmed (gray), negative (white), and modified (reticulated) by WES and reverse phenotyping. (B) Inner pie chart: distribution of patients according to the eight clinical categories based on pre-WES clinical evaluation (podocytopathies, collagenopathies, CKDu, tubulopathies, ciliopathies, CAKUT, syndromic CKD, metabolic kidney disorders). Outer pie chart: percentage of diagnosis confirmed (solid), modified (reticulated), and negative (white) in patients belonging to the eight clinical categories. (C) Percentage of diagnosis obtained with WES alone (light green), WES coupled with reverse phenotyping in the patient (striped), and WES coupled with reverse phenotyping in the patient and in the family (double striped) of patients belonging to the eight clinical categories. (D) On the left side, the suspected and on the right side, the genetic diagnosis in those patients that underwent disease reclassification after WES. CAKUT, congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract; CKDu, CKD of unknown origin; RPF, reverse phenotyping in the family; RPP, reverse phenotyping in the patient; WES, whole-exome sequencing.