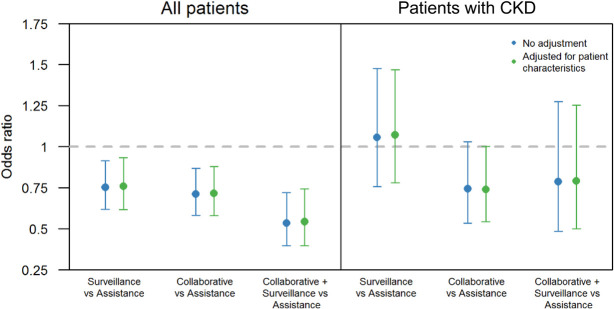
Figure 3.
Multilevel logistic models for AKI with site-level random effects for all cardiac catheterization patients and those patients with CKD. The following patient characteristics were included for adjustment: age, race, tobacco use, anemia, heart failure, CKD, diabetes, hypertension, prior percutaneous coronary intervention, and site baseline performance. In all patients, the Collaborative versus Assistance (with or without Surveillance), Surveillance versus None (for Collaborative or Assistance), and the specific Collaborative+Surveillance intervention cluster compared with Assistance alone showed statistically significant reductions in AKI. In the latter, the adjusted and unadjusted odds ratios were 0.54 [0.40–0.74] and 0.54 [0.40–0.72], respectively. Surveillance, Automated Surveillance Reporting; Assistance, Technical Assistance; Collaborative, Virtual Learning Collaborative.