Figure 6.
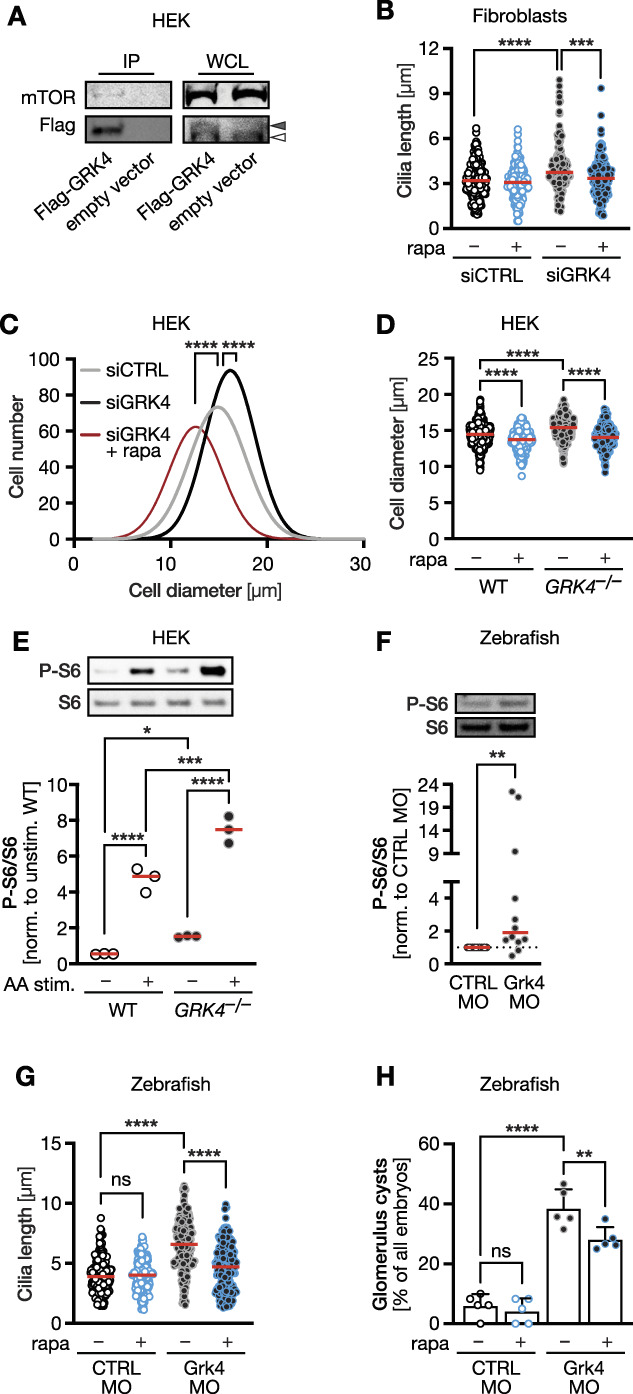
GRK4 negatively regulates mTOR signaling. (A) Co-IP experiments in control- or Flag-tag GRK4-transfected HEK293 cells demonstrating an interaction with endogenously expressed mTOR. Representative blots of one of three Co-IPs. Open arrowhead indicates nonspecific band in Flag-blot, filled arrowhead GRK4 band. (B) Cilium length in human fibroblasts is normalized by the mTOR pathway inhibitor rapamycin. n=190 (siCTRL), 173 (siCTRL+rapa), 152 (siGRK4), and 156 (siGRK4+rapa) cilia. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn multiple comparison test, ****P< 0.0001, ***P< 0.001. (C) HEK cells depleted of GRK4 are larger. Rapamycin treatment rescues cell size. n=398 (siCTRL), 473 (siGRK4), and 328 (siGRK4+rapa) cells. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn multiple comparison test, ****P< 0.0001. (D) GRK4 knockout HEK cells have a larger diameter, which is rescued by rapamycin. n=518 (WT), 465 (WT+rapa), 483 (GRK4−/−), and 326 (GRK4−/−+rapa) cells. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn multiple comparison test, ****P<0.0001. (E) mTOR pathway activity as measured by S6 phosphorylation is elevated in the absence of GRK4. n=4 experiments. One-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak multiple comparison test. ****P<0.0001, ***P=0.0003, *P=0.0438. (F) Twenty four hpf zebrafish embryos depleted of Grk4 display higher mTOR pathway activity. n=4 experiments. Two-tailed Wilcoxon rank test. **P=0.0068. (G) Rapamycin reduces the cilium length in the pt of zebrafish depleted of Grk4. n=165 (CTRL MO), 167 (CTRL MO=rapa), 215 (siGRK4), and 234 (siGRK4+rapa) cells. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn multiple comparison test, ****P<0.0001. (H) Rapamycin partially rescues cyst formation in Grk4 morphant embryos. n=5 experiments with 69 (CTRL MO), 78 (CTRL MO=rapa), 81 (siGRK4), and 84 (siGRK4+rapa) embryos analyzed. One-way ANOVA test with Sidak multiple comparison test, ****P<0.0001, **P=0.0093. Red line indicates median in (B) and (D)–(H). WCL, whole cell lysate.
