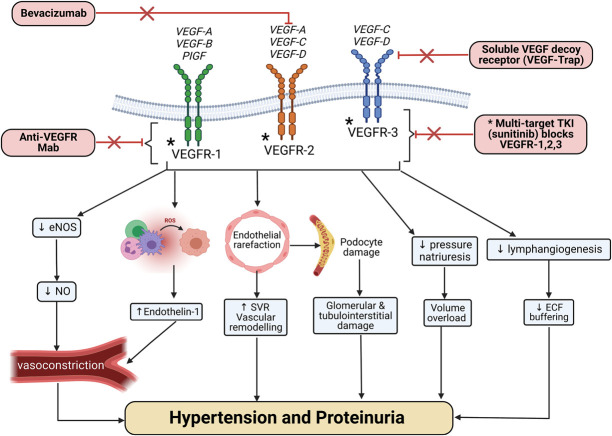
Figure 1.
Mechanism of action of the different VEGF signaling pathway inhibitors agents and the pathophysiologic changes leading to hypertension and proteinuria. ECF, extracellular fluid; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; Mab, monoclonal antibody; NO, nitric oxide; PlGF, placental growth factor; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SVR, systemic vascular resistance; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.