Figure 1.
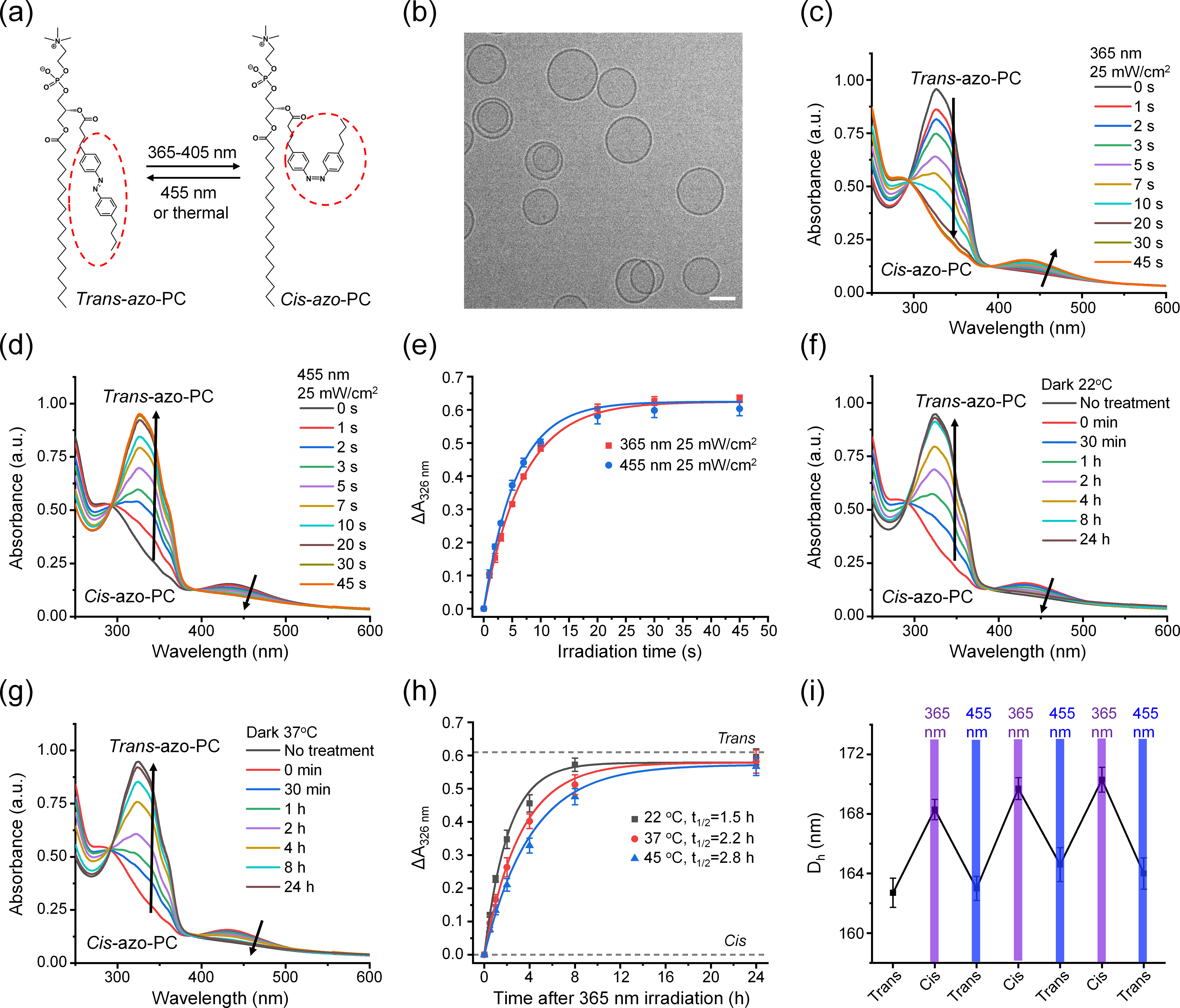
Photophysical properties of asozomes. (a) Schematic of the photoisomerization of azo-PC. (b) Cryo-TEM image of azosomes. Scale bar: 100 nm. (c) and (d) UV–Vis spectra change of azosome upon the irradiation of (c) 365 nm light and (d) 455 nm light. (e) The absorbance change of azosome at 326 and 455 nm light as a function of irradiation time. (f) and (g) UV–Vis spectra change of azosome in the dark at (f) 22 °C and (g) 37 °C. 365 nm light irradiation (25 mW/cm2, 60 s) was performed on the azosome to switch trans-azo-PC to cis-azo-PC at 0 min. (h) The absorbance change of azosome at 326 nm over time in the dark at 22, 37 and 45 °C. The data were fit based on a first-order reaction to give the half-life of cis-azo-PC. (i) The Z-average hydrodynamic diameter of azosome (azo-PC: 25%) measured by dynamic light scattering (DLS) under photoisomerization of azo-PC. 365 or 455 nm light was irradiated on the azosome for 30 s at 25 mW/cm2.
