Figure 4.
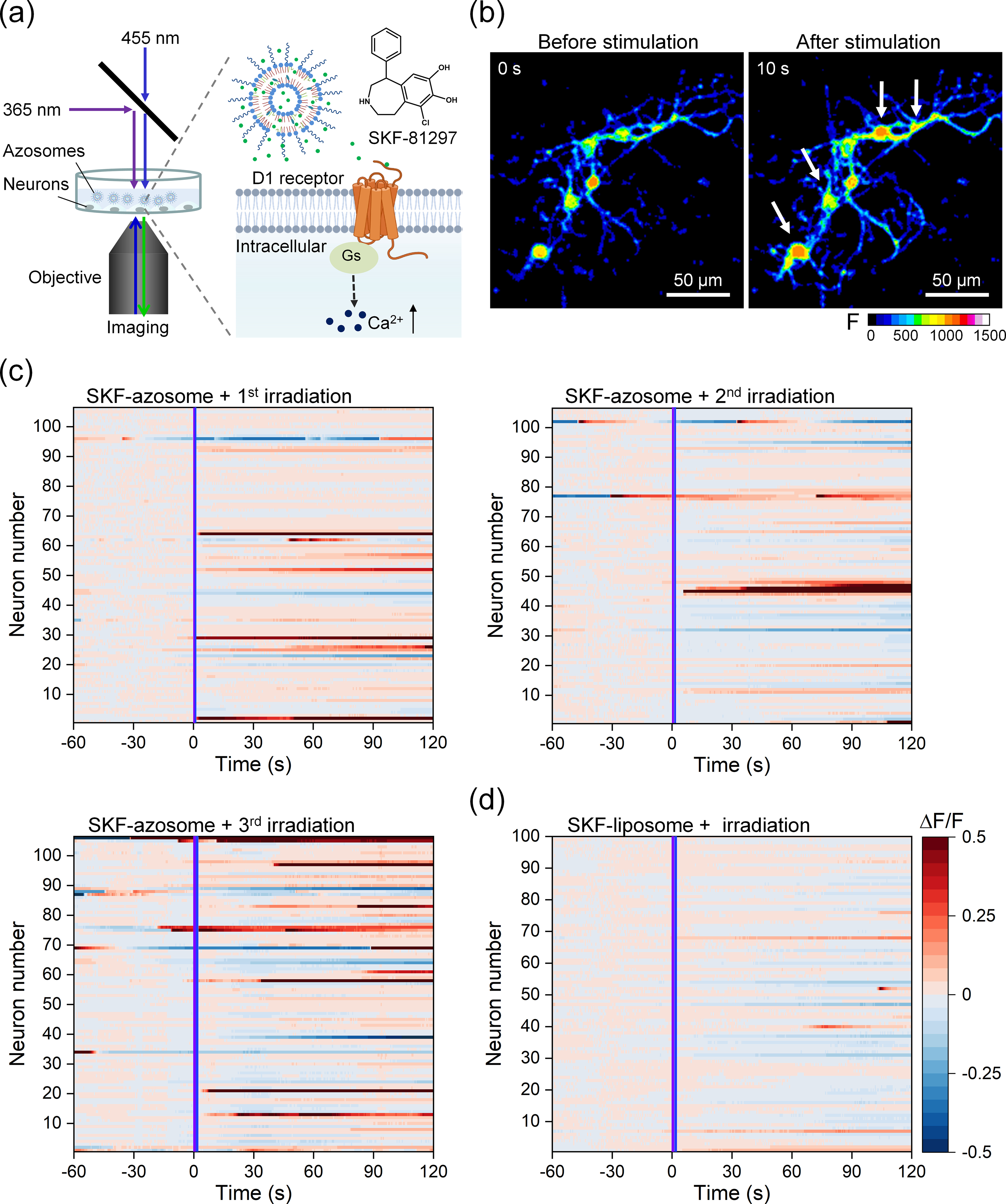
Controlled release of a D1 receptor agonist for neuromodulation. (a) Schematic photorelease of SKF-81297 from the azosome to induce Ca2+ elevation in primary mouse striatal neurons. (b) Real-time fluorescent images of primary mouse striatal neurons before and after the irradiation of sequential 365 nm light and 455 nm light. Fluo-4 was used as the Ca2+ indicator. Scale bar: 50 μm. (c) and (d) The fluorescence change (ΔF/F) plotted as a function of time from individual neurons incubated with (c) SKF-azosome or (d) SKF-liposome. The irradiation of 365 and 455 nm light was performed during the imaging at 0 s. Three repeated irradiations (25 mW/cm2) were performed on SKF-azosome with an interval of 10 min (1st, 365 nm 0.3 s + 455 nm 0.3 s; 2nd, 365 nm 0.5 s + 455 nm 0.5 s; 3rd, 365 nm 1 s + 455 nm 1 s). The irradiation condition (25 mW/cm2) in (d) was 365 nm 1 s + 455 nm 1 s. The activated neuron was counted if the mean fluorescence change (ΔF/F) after stimulation was larger than the mean + 3δ (δ: standard deviation) of baseline. The neurons were labeled in the same order in (c).s
