Figure 5. Preconditioning with different volumes of exercise sustain neurotrophic and neuroenergetic brain reserves thirty days after severe traumatic brain injury.
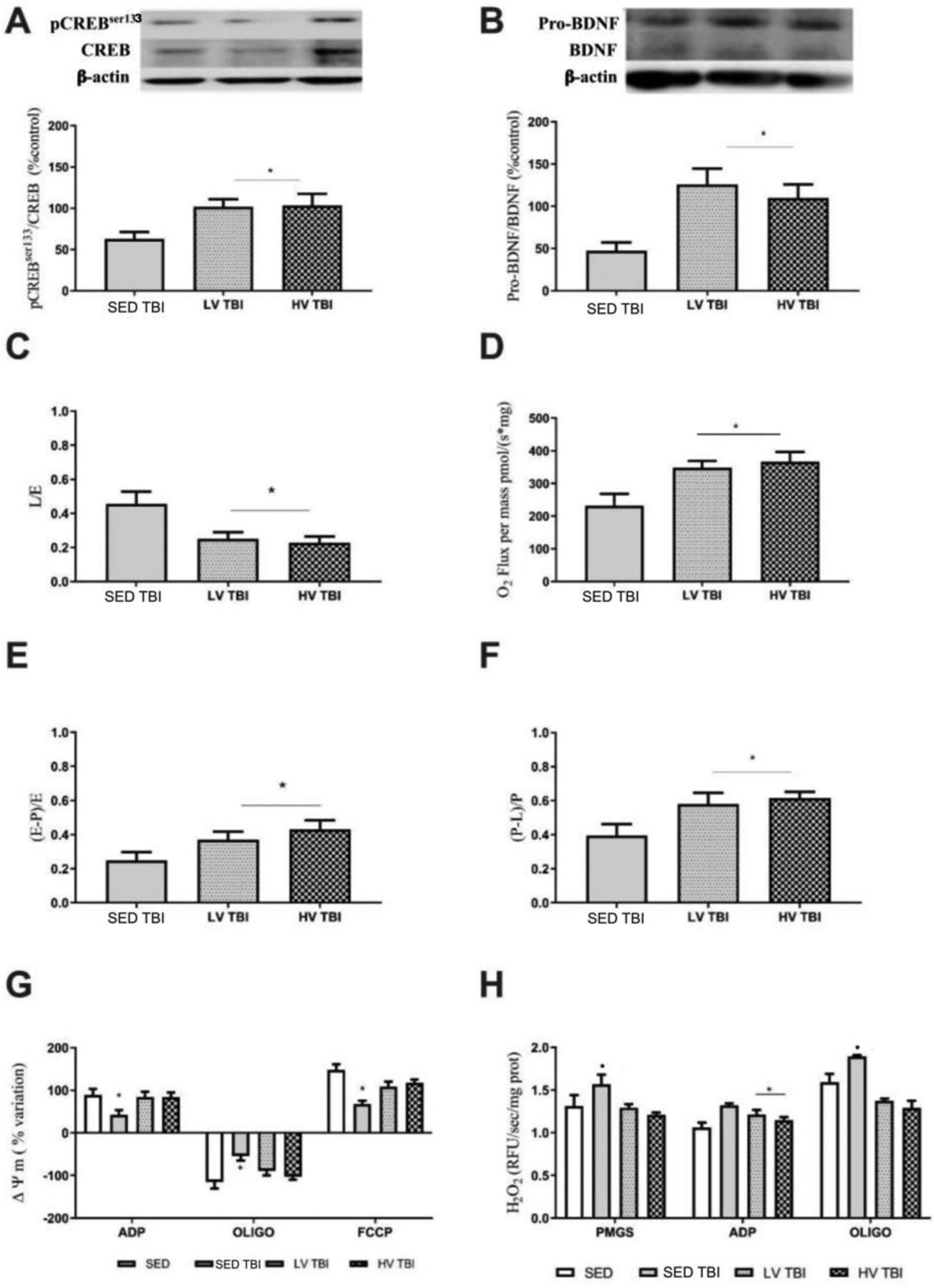
Engagement in lower and higher exercise volumes (LV and HV, respectively) prior to TBI sustained the hippocampal levels of pCREBSer133/CREB (A) and pro-BDNF/BDNF (B). The mitochondrial bioenergetic endpoints including leak respiration (C), maximal ETS capacity (D), biochemical coupling efficiency (E) and the OxPhos capacity (F) was significantly improved in LVTBI and HVTBI relative to SEDTBI group. Mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) and mitochondrial H2O2 production was improved in LVTBI and HVTBI groups (G and H, respectively). Pointed lines in A, B, C, D, and F represent the values of SED group (n=8 per group). * Denotes difference from SEDTBI group when p < 0.05). Abbreviations: LV, lower exercise volume; HV, higher volume; SED, sedentary; OxPhos, oxidative phosphorylation.
