Figure 7. Effects of lower- and higher physical exercise volumes and severe traumatic brain injury on spatial memory.
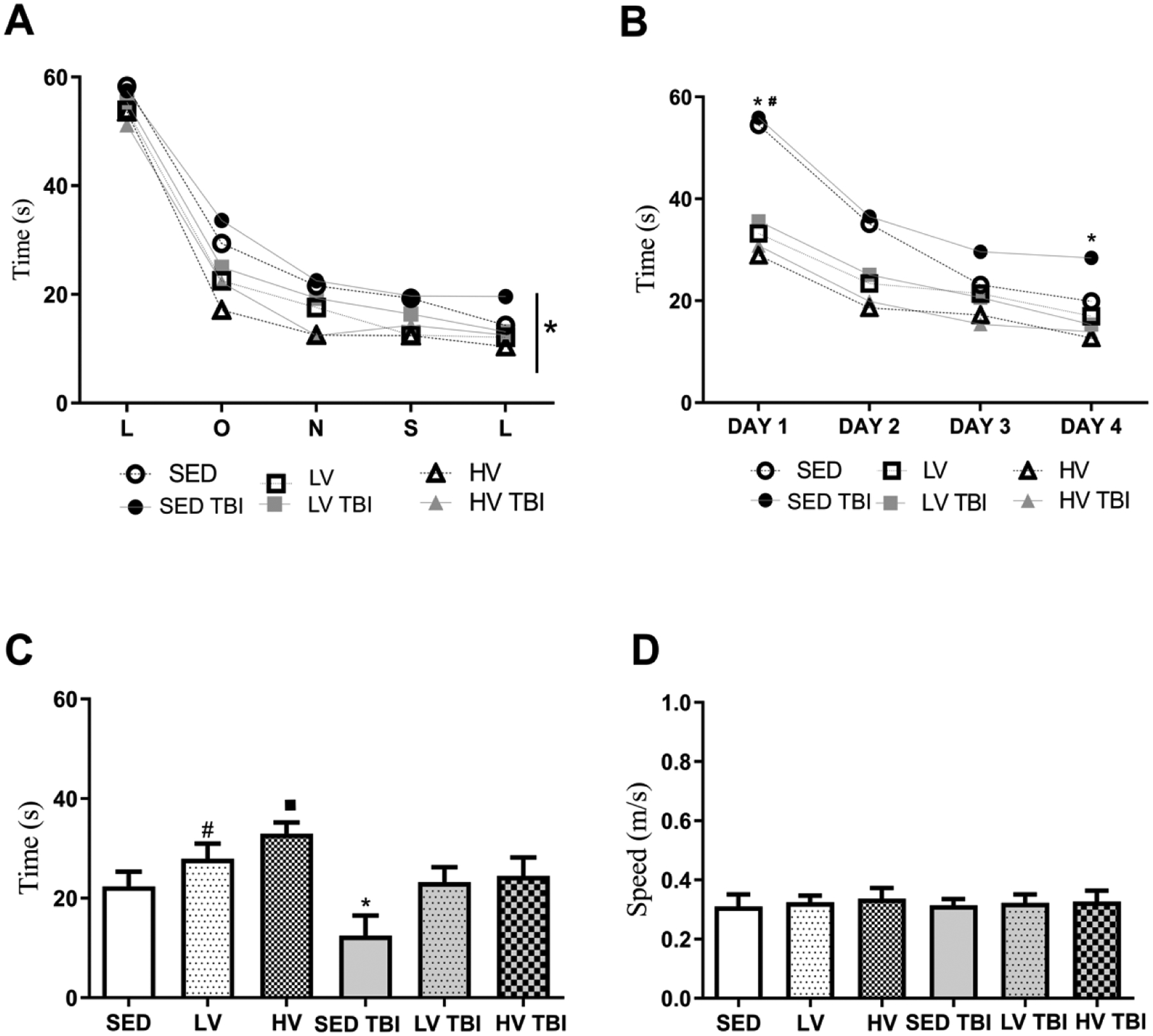
All groups learned to find the platform in the flag test (A). In the acquisition phase of the Morris water maze task (MWM), the SEDTBI group spent more time searching for the hidden platform than other groups (B). In the test phase without the platform, both exercised groups (LV and HV) spent more time in the quadrant zone than SED groups but the memory performance of HV group was significantly more pronounced than LV. SEDTBI displayed decrease in the time spent in the quadrant zone but mice submitted to exercise preconditioning (LVTBI and HVTBI) showed attenuation of this memory deficit (C). The swimming speed was similar between groups (D) (n=8 per group). # Denotes statistical difference from SED. # Denotes statistical difference from SED and LV groups. * Denotes significant difference from other groups. Abbreviations: LV, lower exercise volume; HV, higher volume; SED, sedentary; OxPhos, oxidative phosphorylation; TBI, traumatic brain injury.
