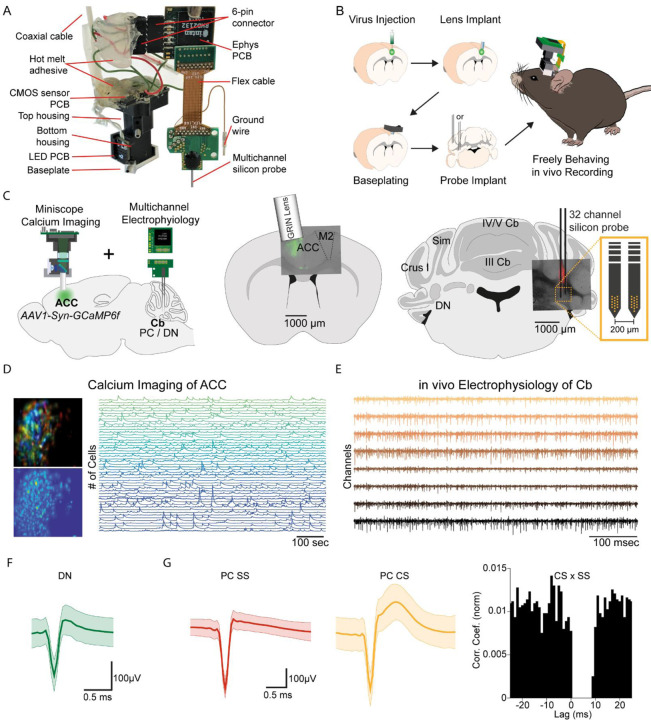
Figure 1. E-Scope: an integrated device allowing synchronous calcium imaging of anterior cingulate cortex and electrophysiological recordings in cerebellum.
(A) Photograph of E-Scope hardware. The multichannel silicon probe (32 channels) connects to the custom Ephys PCB. The Ephys PCB is connected to the CMOS sensor PCB of the Miniscope via a 6-pin connector. The electrophysiology and image data streams are both conveyed through the coaxial cable. (B) Illustration of the process for implanting the E-Scope. (C) Illustrations and photomicrographs showing the location of AAV1-Syn-GCaMP6f virus injection in ACC (left, mid) and multichannel probe implant in the dentate nucleus of the cerebellum (left, right). (D) Pseudo-color (top left) and averaged activity heatmap from calcium imaging ACC neurons segmented using CNMF-E (bottom left). Calcium signals from neurons shown on the left (right). (E) in vivo extracellular electrophysiology recording of PCs in the cerebellum (Cb). (F) Average spike waveform of a dentate nucleus (DN) neuron. (G) Average simple spike (SS) waveform (left) and average complex spike (CS) waveform (mid) of a PC. Cross-correlogram of simple spikes and complex spikes shows the pause in simple spike activity after a complex spike (right).