Fig 1. AML cells exhibit a similar phenotype to HAM when compared to MDM.
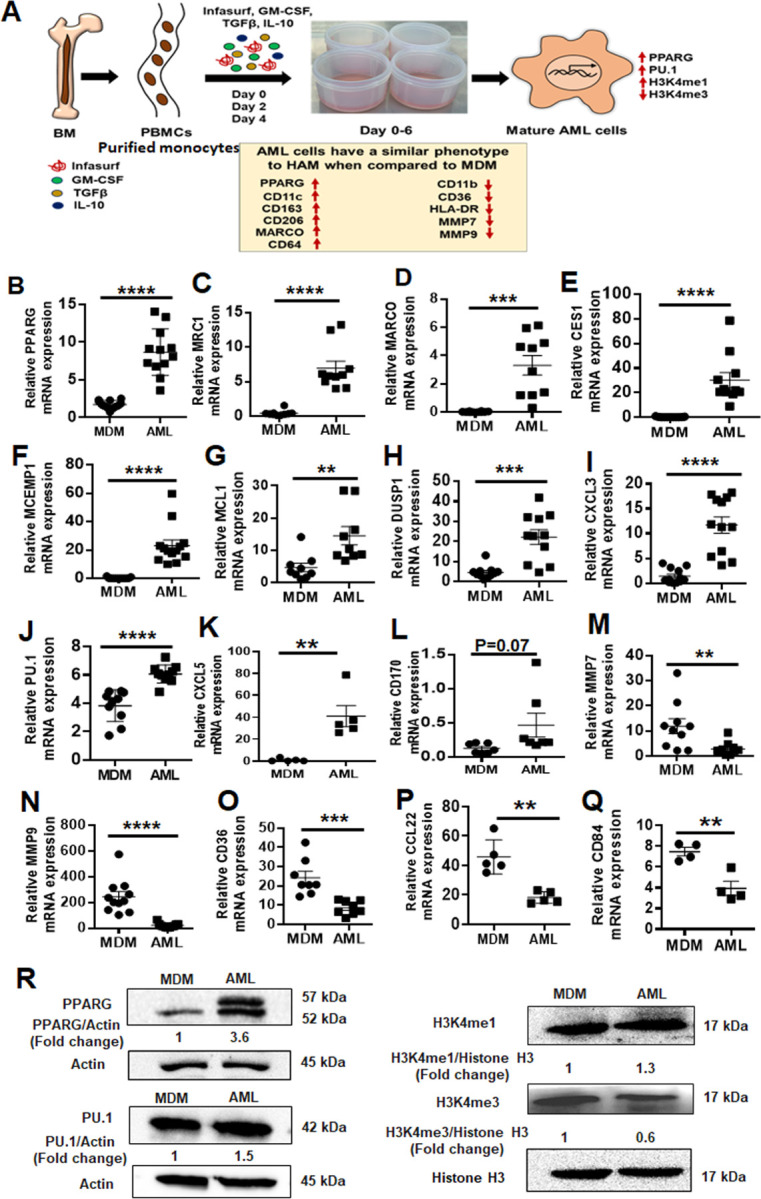
(A) Model of in vitro generation of human Alveolar Macrophage-Like (AML) cells from human PBMCs. Healthy human PBMCs were exposed (Day 0, 2, 4) to lung-associated components [surfactant (Infasurf) and cytokines (GM-CSF, TGF-β, IL-10)] (“ALL cocktail”) for 6 days or left untreated (MDM). AML cells demonstrated a similar phenotype to HAM (17, 21) compared to MDM with indicated higher (red upside arrow) and lower (red downside arrow) cell surface expression. AML cells and HAM have similar transcriptional profiles with increased expression of PPARG and PU.1 (SPI1). Like HAM (17, 21), AML cells express specific histone modifications and methylation with high H3K4me1 and low H3K4me3. (B-Q) PBMCs were exposed to ALL cocktail for 6 days on alternative days (Day 0, 2, 4) or left untreated (MDM). qRT-PCR data demonstrate significant increases in (B) PPARG, (C) MRC1, (D) MARCO, (E) CES1, (F) MCEMP1, (G) MCL1, (H) DUSP1, (I) CXCL3, (J) PU.1 (SPI1), (K) CXCL5 and (L) CD170 and decreases in (M) MMP7, (N) MMP9, (O) CD36, (P) CCL22 and (Q) CD84 expression in AML cells compared to untreated MDM. Gene expression was normalized to Actin. Representative dot plots showing relative mRNA expression of the indicated genes from 12–15 human donors. Each dot indicates individual donors. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM and analyzed by Unpaired Student’s ‘t’ test ** p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001, ****p≤0.0001. (R) AML cells demonstrate a HAM-like phenotype, with increased expression of PPARG, PU.1, H3K4me1 and decreased expression of H3K4me3. Nuclear extracts were collected and Western blot performed to assess expression of PPARG, PU.1, H3K4me1 and H3K4me3. Actin and Histone H3 were used as loading controls. Representative blots from n=4, numbers below each blot indicate mean fold change relative to MDM.
