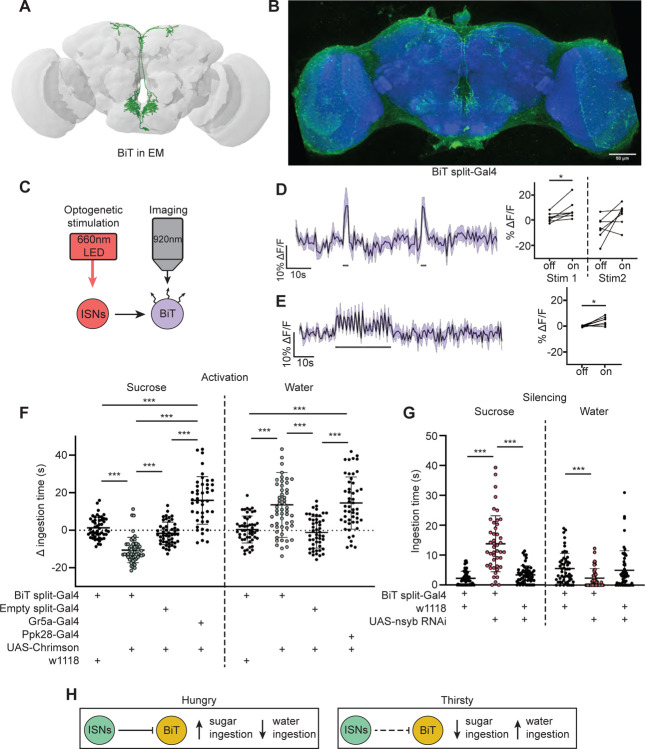
Figure 2. ISNs inhibit BiT, which oppositely regulates sugar and water ingestion.
(A) BiT neuron reconstruction from FAFB dataset. (B) Light microscopy image of BiT split-Gal4. (C) Experimental setup for in vivo voltage imaging. We expressed the light sensitive ion channel Chrimson in the ISNs and optogenetically stimulated them with 660nm LED. We expressed the voltage sensor ArcLight in BiT and imaged it with a 2 photon microscope. (D) ArcLight response of BiT soma to 2s optogenetic stimulation of the ISNs or (E) 30s optogenetic stimulation of the ISNs. Left: Scatter plot shows mean +/− SEM of all flies imaged, gray bars represent LED stimulation. Right: Quantification of mean fluorescence intensity before stim (off) and during stim (on), each dot represents one fly. Paired Wilcoxon and paired t-test (Stim 2, p=0.07). n=7 flies. (F) Temporal consumption assay for 1M sucrose or water during acute optogenetic activation of BiT with Chrimson. Ingestion time of females exposed to light normalized to dark controls of indicated genotype. Sucrose: Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparison test. Water: One-way ANOVA with Holm-Šídák multiple comparison test. n=44–54 animals/genotype.(G) Temporal consumption assay for 1M sucrose or water using RNAi targeting nSyb in BiT. Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s multiple comparison test. n=45–57 animals/genotype. (H) Neural model for BiT coordination of sucrose and water intake. Dashed lines indicate inactive synapses. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001