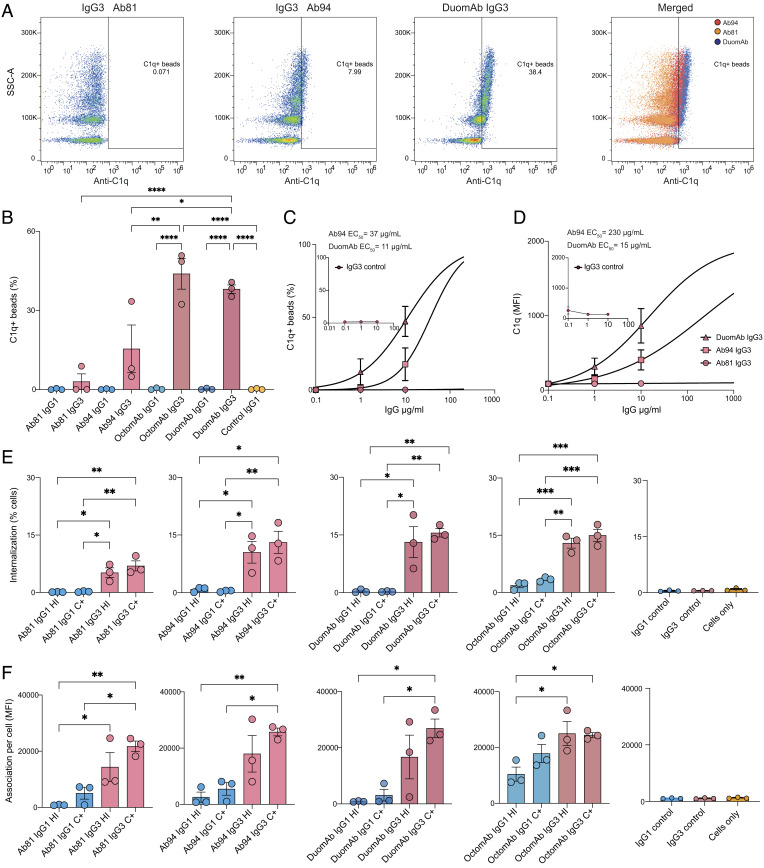
Fig. 3.
IgG subclass and oligoclonality affect complement activation and phagocytosis of spike beads by neutrophils. (A) Individual gates for C1q deposition for Ab81, Ab94, and OctomAb IgG3 at 10 µg/mL. The far-right panel shows all three plots merged. (B) shows data on C1q deposition for the indicated monoclonals and oligoclonal cocktails. (C) Percentage of C1q deposition as a function of antibody concentration with EC50 values in the graph. (D) Fluorescent signal of deposited C1q as a function of antibody concentration with EC50 values present in the graph. In C and D, IgG3 isotype control data are shown as a small graph in each respective graph. (E) Neutrophils with internalized spike-beads comparing different treatments and heat-inactivated serum (HI) with complement-active serum (C+). (F) Bead signal of neutrophils associated with beads (APC+, SI Appendix, Fig. S2D). (E and F) Isotype controls are shown furthest to the right. Three independent experiments were performed for A–E. For A–E, statistical analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA and correction for multiple comparisons was done with Tukey’s test. * denotes P value below 0.05, ** denotes P value below 0.01, *** denotes P value below 0.001, and ns denotes a P value above 0.05.