Figure 1.
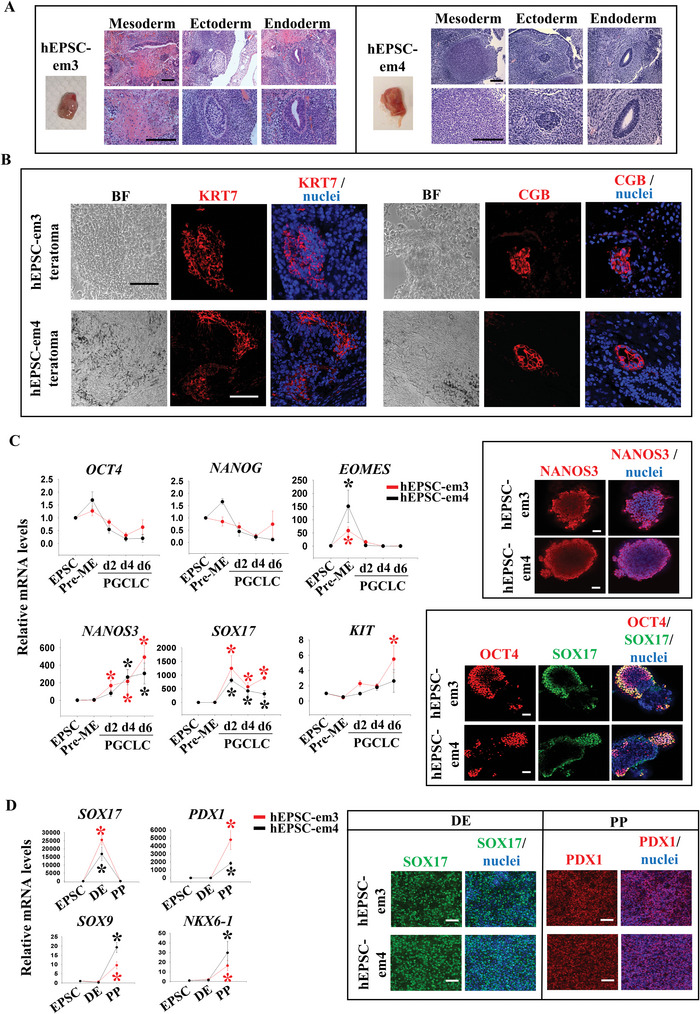
Establishment of EPSC from human pre‐implantation embryos (hEPSC‐em). A) Haematoxylin and eosin staining of teratoma sections derived from hEPSC‐em3 (left) and hEPSC‐em4 (right). Bone cartilage or striated muscle structure (mesoderm), neural tissue structure (ectoderm), and glandular epithelium structure (endoderm) were observed. Scale bar: 100 µm. B) Immunofluorescence staining of trophoblast markers (KRT7 and CGB) on teratoma sections derived from hEPSC‐em3 (top) and hEPSC‐em4 (bottom). The nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33258. Scale bar: 100 µm. C) RT‐qPCR analysis of OCT4, NANOG, EOMES, NANOS3, SOX17, and KIT during PGCLC formation from hEPSC‐em (left). *p < 0.05 compared to EPSC control, t‐test; n = 3. Immunofluorescent staining of PGC markers (NANOS3, SOX17, and OCT4) following 6 days of PGCLC induction (right). The nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33258. Scale bar: 100 µm. D) RT‐qPCR analysis of DE marker (SOX17) and PP markers (PDX1, SOX9, and NKX6‐1) during pancreatic differentiation from hEPSC‐em (left). *p < 0.05 compared to EPSC control; t‐test; n = 3. Immunofluorescence staining of pancreatic markers (SOX17 and PDX1) following pancreatic differentiation from hEPSC‐em (right). The nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33258. Scale bar: 100 µm. DE: definitive endoderm, PP: pancreatic progenitor.
