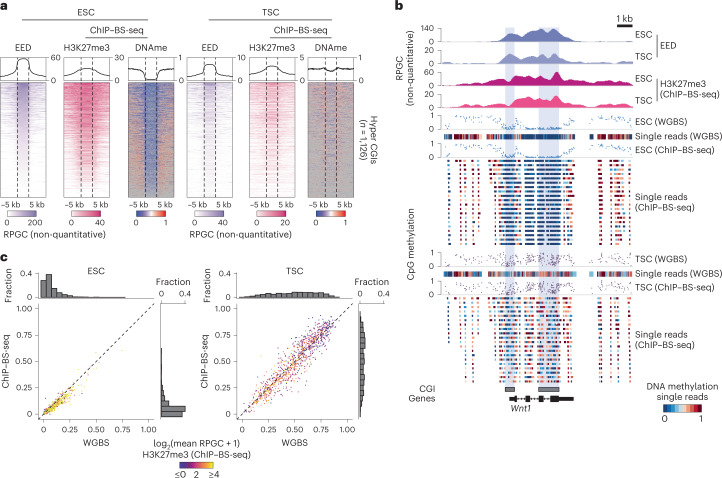
Fig. 3. TSC chromatin is dually modified by H3K27me3 and DNA methylation at equilibrium.
a, Metaplots and corresponding per-locus heat maps of EED (ChIP–seq), H3K27me3 (ChIP–BS-seq) and DNA methylation (ChIP–BS-seq) for hyper CGIs. ESCs display the expected inverse correlation between DNA methylation and H3K27me3, which is consistent with local enrichment of EED over these CGIs. TSCs also show local enrichment of EED over CGIs, but the canonical relationship between H3K27me3 and DNA methylation is lost and these modifications co-occupy the same loci. TSC ChIP signal is somewhat diminished in comparison with ESCs, probably due to increased global enrichment for this enzyme and its associated modification throughout the TSC genome. b, Genome browser track of the Wnt1 locus in ESCs and TSCs for EED and H3K27me3 (as measured by ChIP–BS-seq) enrichment alongside DNA methylation as measured by WGBS and ChIP–BS-seq. Average read-level methylation is expanded for ChIP-BS-seq data below the summary track (only the first 20 rows are shown, reads must have three or more CpGs to be included). Read-level analysis confirms that the diffuse, high entropy nature of DNA methylation in TSCs occurs within H3K27me3-modified nucleosomes. c, Scatter plot comparing the average methylation level of hyper CGIs as measured by WGBS and ChIP–BS-seq, coloured by the average H3K27me3 ChIP–BS-seq signal. WGBS includes no enrichment step and acts effectively as background; its high correlation with ChIP–BS-seq supports a model where intermediate DNA methylation in TSCs co-exists with H3K27me3 nucleosomes at equilibrium.