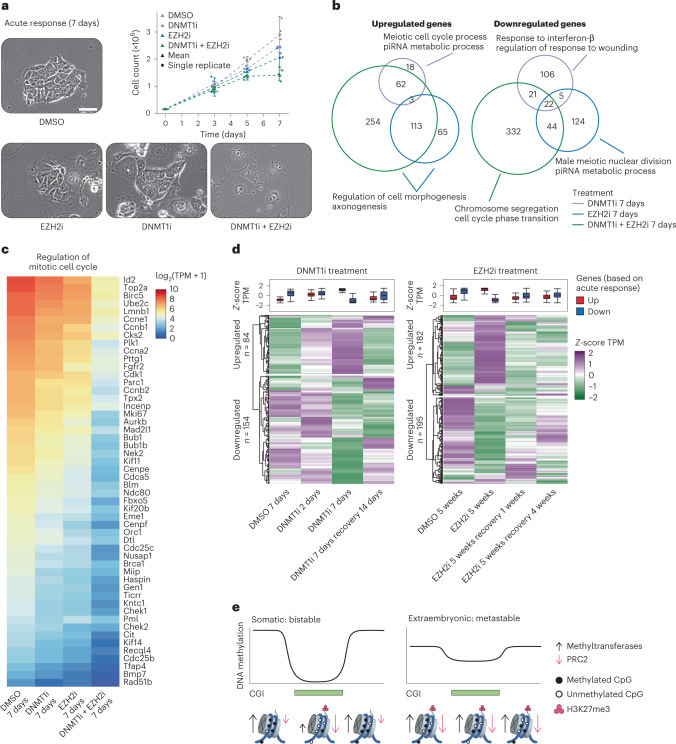
Fig. 6. Transcriptional response to epigenetic inhibitors.
a, Brightfield images of control and inhibitor treated TSCs. Top right: cell counts over 7 days of treatment (n = 3 biological replicates from independent experiments per condition, error bar reflects standard deviation). TSCs tolerate either DNMT1i or EZH2i, but dual inhibition has severe effects on morphology and proliferation (scale bar, 50 µm). b, Overlap of up- and downregulated genes between DNMT1i, EZH2i and combined treatment with select GO term enrichments for each gene set (piRNA, PIWI-interacting RNA). Notably, combined treatment significantly downregulates a large set of genes associated with cell cycle progression. A full list of top GO terms is presented in Extended Data Fig. 9a. c, Heat map visualizing gene expression (log2-transformed TPM) associated with regulation of mitotic cell division in DMSO-, DNMT1i-, EZH2i- and double inhibitor-treated cells. Treatment with both inhibitors leads to significantly reduced expression of these genes (only differentially expressed genes are shown). The effect is milder in single inhibitor treatments. d, Heat map and box plots of differentially expressed genes during DNMT1i (left) and long-term EZH2i (right) treatment including recovery timepoints (number of genes indicated in the figure, differentially expressed genes are identical to those in Fig. 5b). In both cases, the transcriptional response is largely reversible following inhibitor washout. Lines denote the median, edges denote the IQR and whiskers denote either 1.5× IQR or minima/maxima (if no point exceeded 1.5× IQR; outliers were omitted). e, Simplified model of DNA methylation and PRC2 dynamics in somatic cells compared with the dynamic epigenome found in TSCs. Somatic cells generally regulate genetic loci in a bistable fashion, preserving an overall highly methylated genome and unmethylated CGIs that are protected from DNMT3’s by PRC2. In TSCs, the genome shifts to an overall intermediate, seemingly metastable methylation state, which co-occurs with PRC2-deposited H3K27me3. Although this state can be driven to high or low methylation levels by modulating these two inputs, this form of genome regulation is robust enough to return to the steady-state levels even after long spans of inhibition.