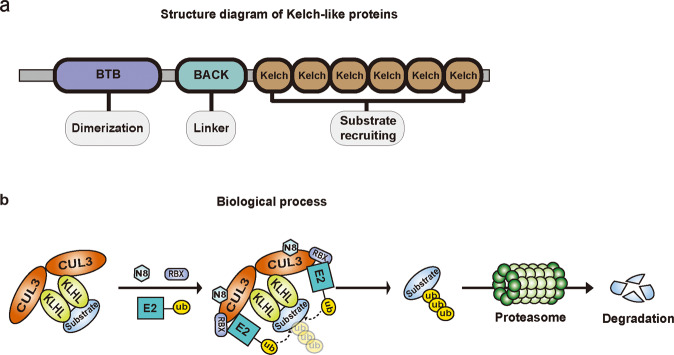
Fig. 1. The KLHLs structure and the biological process regulated by KLHLs.
a Schematic representation of KLHLs structure. KLHLs consist of BTB/POZ domain, BACK domain and Kelch domain. The BTB/POZ domain is essential for dimerization and contributes to CUL3 interaction. The Kelch domain is comprised of six identical motif repeats and mediates specific substrates recruitment. The BACK domain is served as a linker connecting two domains. b The biological process involved in KLHLs regulation. The KLHLs and CUL3 are both dimerized and form CUL3-KLHL complex to identify substrates. The complex then recruits the E2 enzyme when bound to RBX1 and NEDD8, and jointly transfers ubiquitin onto substrates for subsequent proteasome-mediated degradation.