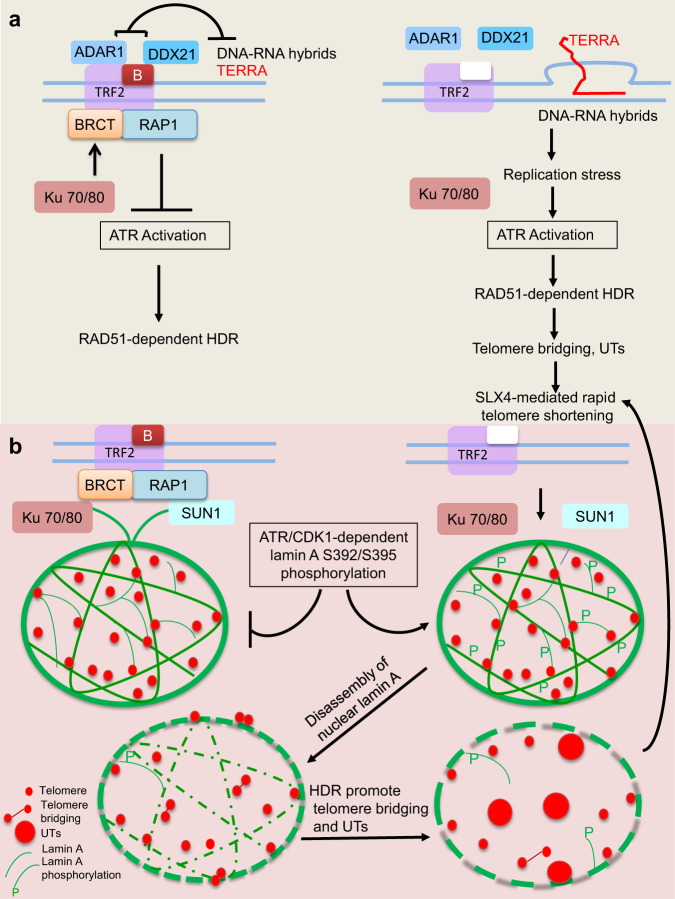
Fig. 8. Speculative schematic diagram illustrating the formation of ultrabright telomeres in the absence of RAP1 and TRF2B.
a In WT cells, TRF2B and RAP1 cooperate to protect chromosome ends from inappropriate activation of ATR-dependent HDR. TRF2B recruits DDX21 and ADAR1p110 to telomeres to resolve DNA-RNA hybrids, preventing the formation of telomeric R-loops, TERRA and UTs. In the absence of RAP1 and TRF2B, stalled replication forks lead to activation of ATR-CHK1, accumulation of telomeric R-loops and TERRA, promoting UT formation. Unresolved telomere recombination intermediates become substrates for cleavage by the SLX4 endonuclease, leading to catastrophic telomere shortening via T-loop HDR and the formation of telomere-free chromosome fusions. b Lamin A acts as a scaffold that restrains telomere movement in the nucleus, possibly through transient associations of RAP1 with KU70/KU80 and SUN1, known NE binding proteins. In the absence of RAP1 and TRF2B, ATR-CHK1 and CDK1 dependent phosphorylation of lamin A results in the disassembly of nuclear lamin A. Decompartmentalization of telomeres due to disruption of the lamin A architecture facilitates HDR, telomere-telomere clustering and UT formation.