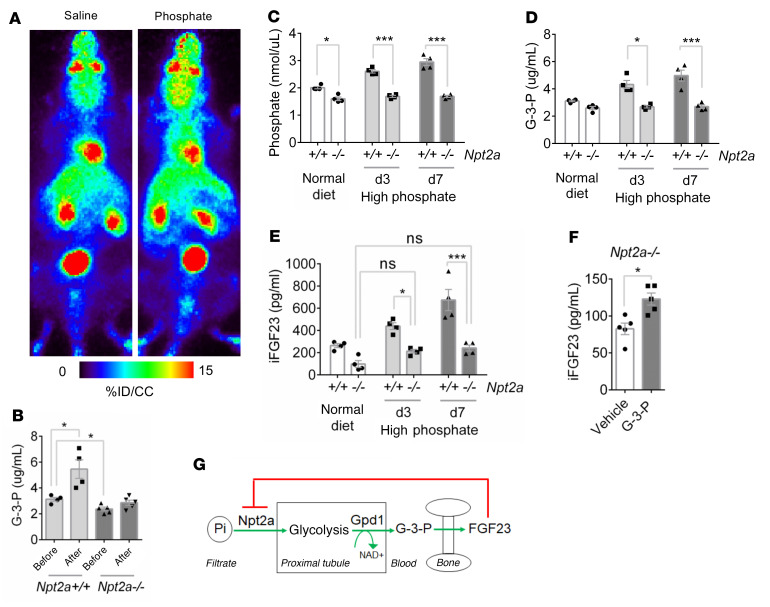
Figure 7. Npt2a is required for kidney glycolytic phosphate sensing.
(A) Representative whole-animal maximum–intensity projection PET scan images 10 minutes after i.v. 18F-FDG and either sodium phosphate or sodium chloride injection of Npt2a–/– mice. (B) Blood G-3-P concentration in Npt2a+/+ and Npt2a–/– mice before and 10 minutes after i.v. sodium phosphate (n = 4–5 per group). (C–E) Blood phosphate (C), G-3-P (D), and intact FGF23 (iFGF23) (E) concentrations in Npt2a+/+ and Npt2a–/– mice fed a normal diet (0.6% Pi) and after 3 and 7 days on high phosphate diet (1.2% Pi) (n = 4 per group). (F) Blood iFGF23 concentration in Npt2a–/– mice 24 hours after i.p. G-3-P (300 mg/kg) or vehicle (n = 5 per group). (G) Schema showing feedback loop with Npt2a mediated phosphate uptake, proximal tubule glycolysis and G-3-P synthesis, and bone FGF23 production with subsequent downregulation of Npt2a. Values are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.0001. ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (B–E) or unpaired student’s t test (F).