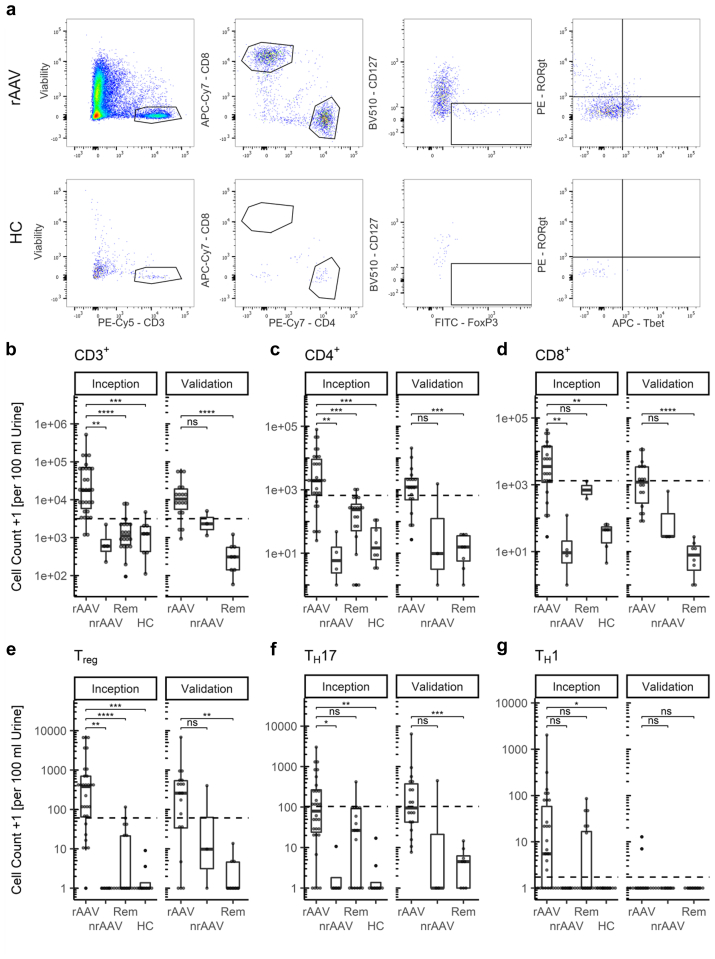
Figure 1.
T cells show distinct, highly elevated subpopulations in urine in renal ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV). (a) Exemplary urinary flow cytometry dot plots of renal active AAV (rAAV) patient and HC, previous gating: even flow, singlets; (b–g) box plots of urinary T cell subpopulations: CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, Treg, TH17, and TH1 cells. Cell counts plotted +1 to visualize zeros on logarithmic scale, statistics were determined using Kruskal-Wallis and post hoc Dunn’s test, P-value summary: ns: P > 0.05, ∗: P = 0.05 – 0.01, ∗∗: P = 0.01 – 0.001, ∗∗∗: P < 0.001. AAV, ANCA-associated vasculitis; ANCA, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies; HC, healthy control, dashed line indicates optimal cut off for identification of rAAV; nrAAV, nonrenal active AAV; rAAV, active renal AAV; Rem, remission; Treg, regulatory T cell; TH17, T helper 17; TH1, T helper 1.