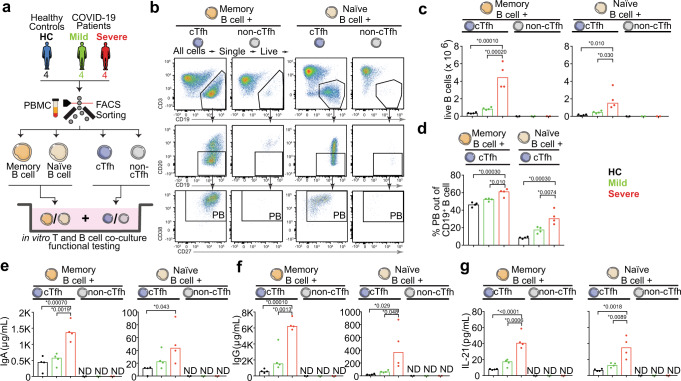
Fig. 4. cTfh isolated from severe COVID-19 patients with acute disease support B cells differentiation and antibody production more efficiently than that from mild COVID-19 patients.
a Blood cTfh, non-cTfh, memory B, and naive B cells were isolated from four severe and mild COVID-19 patients with acute disease, as well as four healthy donors. cTfh or non-cTfh cells were cultured with autologous memory B cells for 6 days, or with autologous naive B cells for 9 days respectively. b Representative example with gating strategy to identify (left) memory B-cell and (right) naive B-cell differentiation. c Bar charts show the number of live B cells in (left) cTfh/non-cTfh co-cultured with memory B cells and (right) cTfh/non-cTfh co-cultured with naive B cells. d Bar charts show the frequency of plasmablast in cTfh-memory/naive B-cell co-cultured. e, f Bar charts show the concentration of (e) IgA and f IgG in supernatant from cTfh/non-cTfh co-cultured with (left) memory B cells and (right) naive B cells. g Bar charts show the concentration of IL-21 in supernatant from cTfh/non-cTfh co-cultured with (left) memory B cells and (right) naive B cells. e–g ND means not detectable. Differences were tested with One-Way ANOVA. P < 0.05 was considered to be a significant difference. *P values <0.05 are listed above each comparison. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.