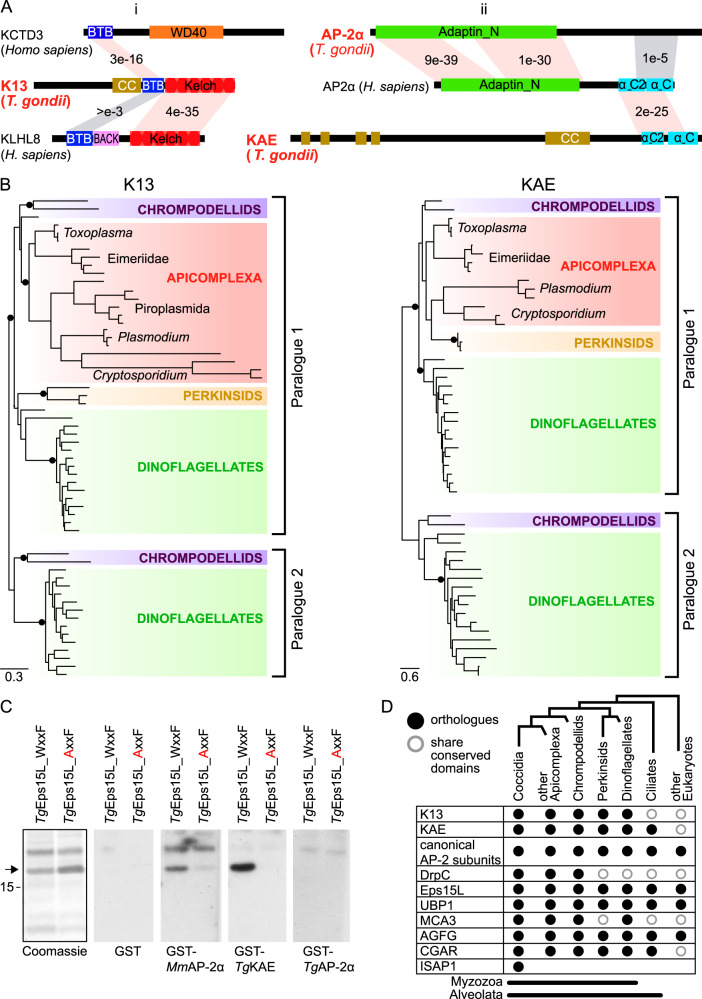
Fig. 7. K13 and AP-2 unique traits co-evolved in Myzozoa.
A Domain architectures of: (i) K13 compared to proteins from humans, which demonstrate high sequence similarity to the BTB and Kelch domains, and (ii) apicomplexan AP-2α and KAE compared to human AP-2α as canonical representative. BLASTP E-values indicate relative conservation between common domains. Conserved domains shown in colour; CC, coiled coil. B Maximum-likelihood phylogenies for K13 and KAE. SH-like aLRT branch supports over 0.9 are indicated by black dots, and complete phylogenies are shown in Fig. S11D. C Far-Western blots with immobilized fragments of TgEps15L (arrow) containing either the native (WxxF) or mutated (AxxF) of the predicted AP-2 ear-binding domain (Coomassie-stained gel, black outline). GST-fused ear domains of AP-2 candidate proteins from Mus musculus (Mm) or T. gondii (Tg) (or GST alone as negative control) were allowed to bind to the Esp15L fragments and visualized by anti-GST staining. The marker size is 15 kDa. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. D Distribution of K13 complex proteins in myzozoan and related lineages.