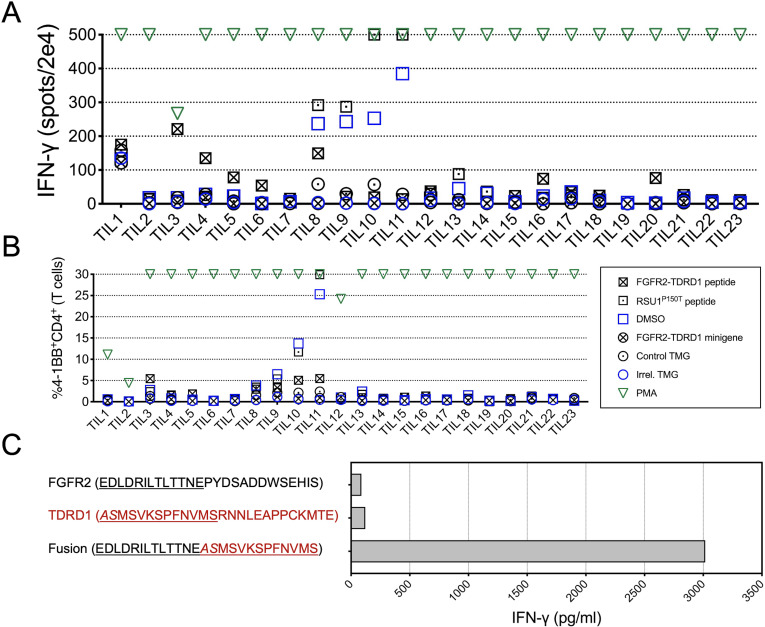
Figure 2.
TILs from patient 1 specifically recognized FGFR2-TDRD1 fusion. (A) TILs (n=23) were co-cultured with autologous DCs that were pulsed with FGFR2-TDRD1 peptide or transfected with FGFR2-TDRD1 minigene. Results of IFN-γ ELISpot are depicted. A tandem minigene (TMG) encoding several point mutations from another patient (Irrel. TMG) and DMSO were used as negative controls for minigene and peptide testing, respectively. A 25-mer peptide representing a point mutation in the RSU1 gene (RSU1P150T), previously identified as a neoantigen, as well as a TMG incorporating this mutation (Control TMG), were used as positive controls. PMA/ionomycin (PMA) was used as a non-specific positive control. (B) Same co-cultures as in (A) were analyzed by flow cytometry for expression of surface activation marker 4-1BB (CD137). The graph depicts the frequency of 41BB+CD4+ cells among all live T cells (a composite of CD8+ and CD4+ cells). (C) TIL3 cells were co-cultured with DCs pulsed with FGFR2-TDRD1 peptide or the control TDRD1 and FGFR2 peptides. IFN-γ production was measured the following day using an IFN-γ electrochemiluminescence assay. DCs, dendritic cells; DMSO, dimethylsulfoxide; ELISpot, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; FGFR2, fibroblast growth factor receptor 2; IFN-γ, interferon gamma;PMA, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate; TDRD1, tudor domain-containing 1; TIL, tumor infiltrating lymphocyte.