Figure 2: RTE mobilization triggers inflammation via cytoplasmic DNA.
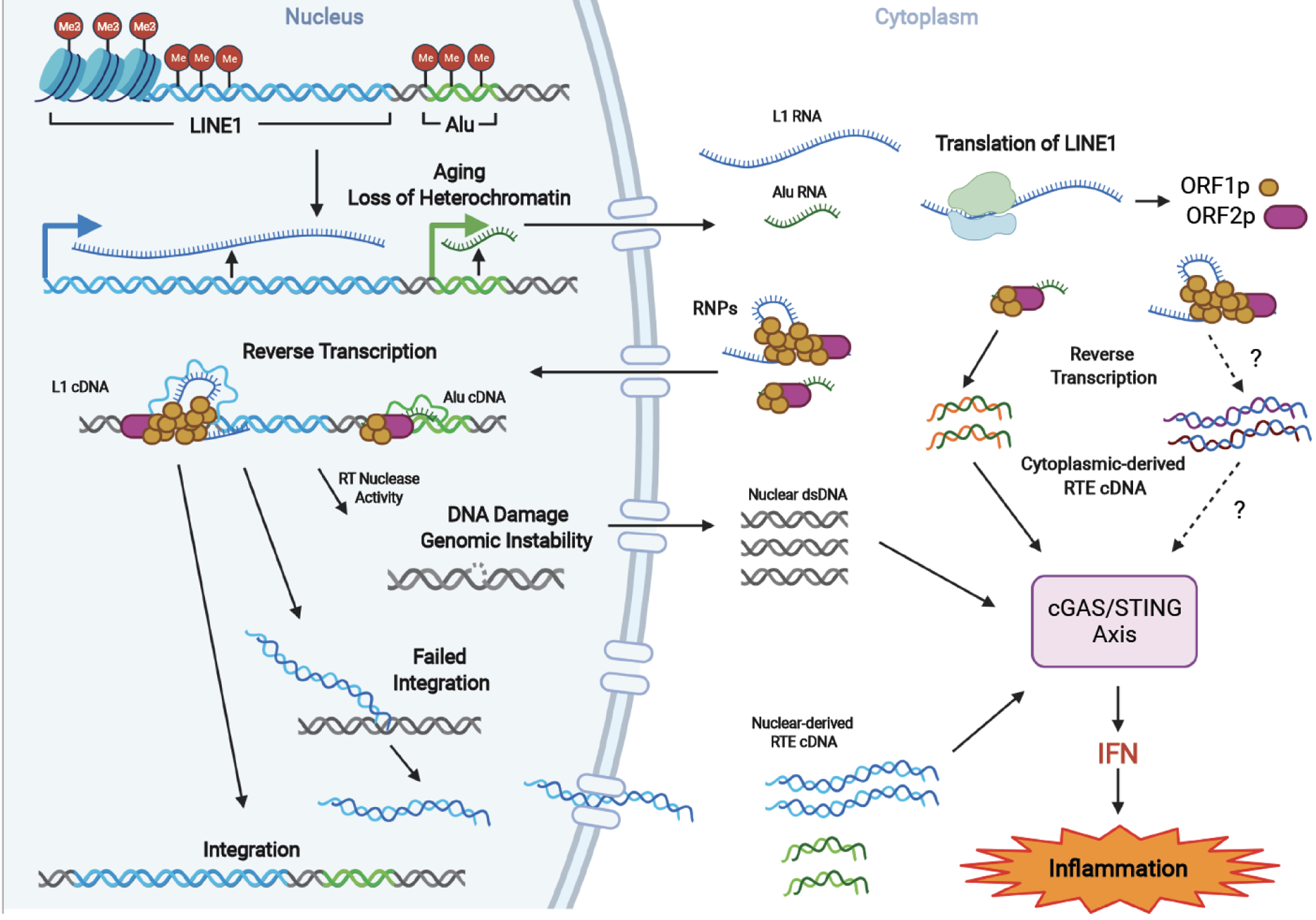
Ageing-related loss of heterochromatin marks on RTEs results in their transcriptional activation and retrotransposition. In the cytoplasm, Alu elements produce ssDNA via self-priming utilizing LINE1 RT machinery. Simar process may take place for L1s. In the nucleus, RNPs initiate RTE integration by generating DNA nicks and reverse transcription, which induces DNA damage. Additionally, unsuccessful integration produces DNA flaps, which are processed to RNA-DNA hybrid fragments. The RTE RNA-DNA hybrids resulting from reverse transcription either in the nucleus or cytoplasm and DNA fragments resulting from genomic damage are recognized by cytoplasmic cGAS, triggering the cGAS-STING signaling, leading to IFN production and sterile inflammation. Dashed lines indicate steps that require further experimental evidence.
