Figure 1:
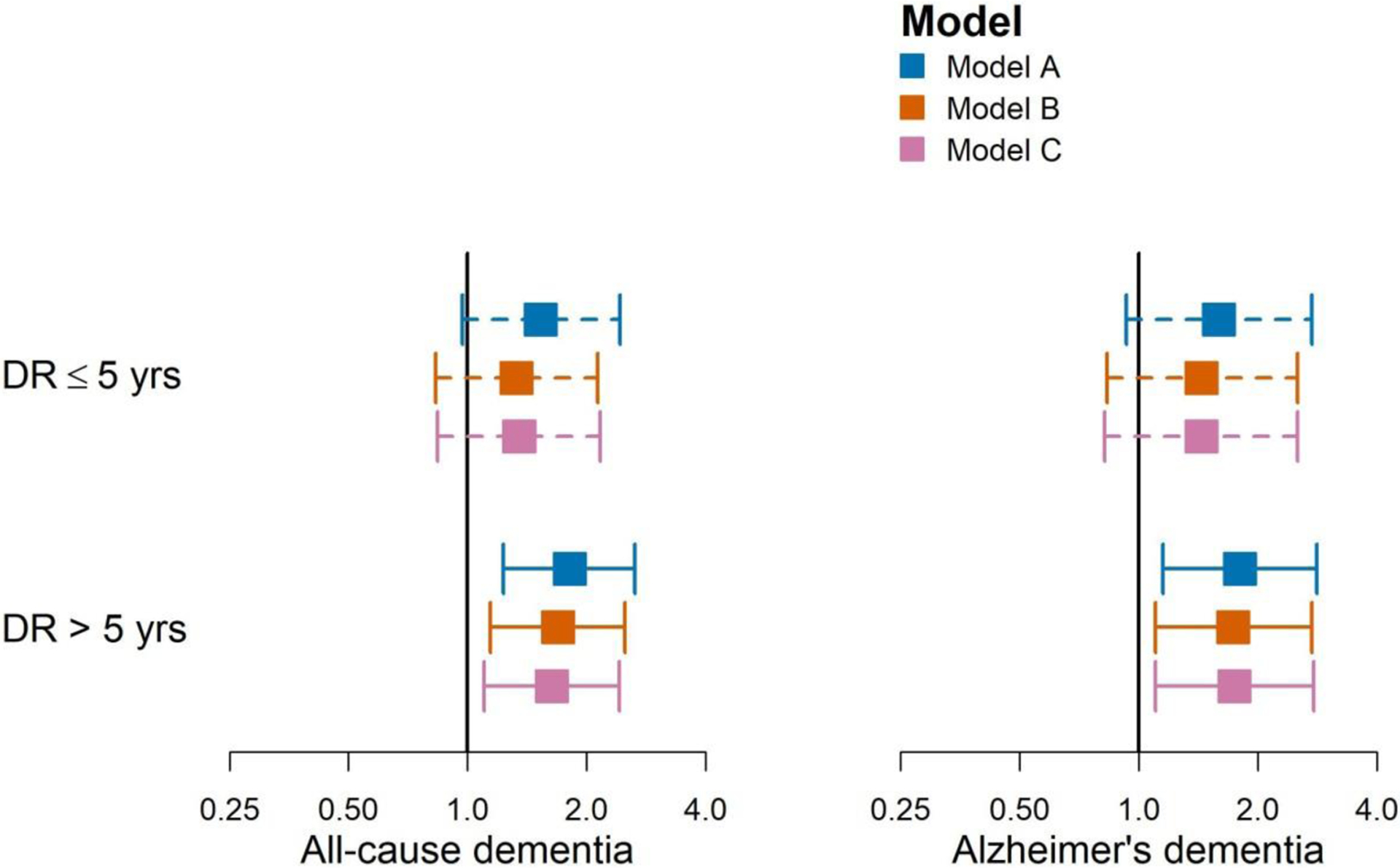
Point estimates (95% CIs) of hazard ratios by diabetic retinopathy (DR) duration. Model A: Model A adjusted for time-varying diabetic retinopathy duration (diagnosis within past 5 years, diagnosis over 5 years ago), glaucoma and age-related macular degeneration duration, age, gender, self-reported non-Hispanic White (yes/no), carrying at least one APOE ε4 allele, degree beyond high school at Adult Changes in Thought (ACT) study entry (yes/no), type of ACT recruitment cohort, and time-varying smoking status (never vs. current/former); Model B: Model A adjusted for microalbuminuria (worst urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio [ACR] status in past 5 years defined as normal/reference with ACR<30 mcg/mg, microalbuminuria with ACR 30–300 mcg/mg, or macroalbuminuria with ACR >300 mcg/mg), long-term glycemia (average glucose over previous 5 years), and renal function based on eGFR measures (3 estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) constructs: average eGFR, eGFR standard error, eGFR trajectory). Model C: Model B adjusted for self-reported history of vascular diseases (heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, congestive heart failure, and hypertension).
