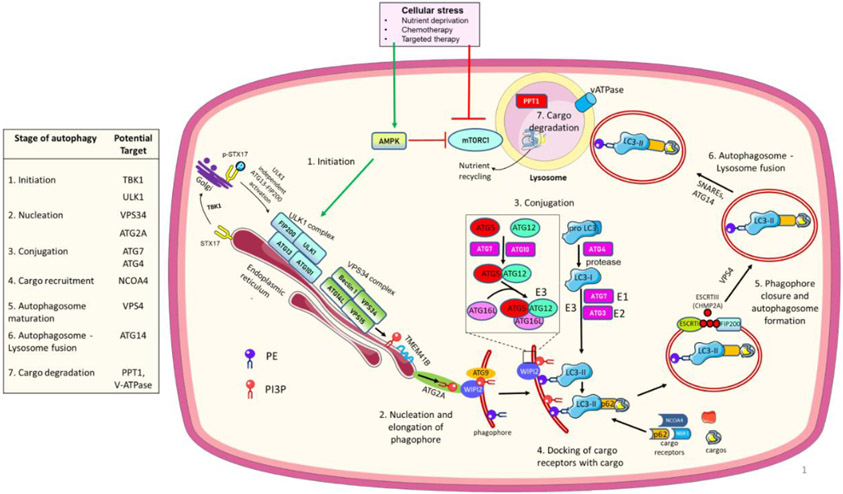
Figure 1. Autophagy regulatory pathway.
Cellular stress activates AMPK which directly and indirectly (through inhibition of mTORC1) activates the ULK1 complex and initiates autophagy. An ULK1 independent activation of autophagy can also occur via TBK1. ULK1 phosphorylates and activates the PI3KC3 lipid kinase complex which generates phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PI3P) to commence phagophore membrane elongation with the help of TMEM41B and ATG2A, which deliver lipids to PI3P-WIPI2 complexes for the next conjugation steps. Two ubiquitin-like sequential conjugation reactions (ATG12 and ATG7 conjugate ATG8 (LC3) protein to phosphatidylethanolamine (PE). ATG7 and ATG3 act as E1 and E2-like enzymes, respectively, and the ATG12-ATG5-ATG16L complex as an E3-like enzyme to finally catalyze the binding of LC3I to PE by ATG3. Next, autophagy cargo receptors with their specific cargos dock onto LC3II in the phagophore/growing autophagosome. ESCRT-III protein polymerization brings together the open ends of the autophagosome which are closed by VPS4 to complete the autophagosome maturation. The autophagosome fuses with the lysosome to degrade and recycle autophagy cargo components. Proteins in the table present potential targets to inhibit different autophagy steps in cancer. For recent advances in each step, please see the main text.