Figure 4.
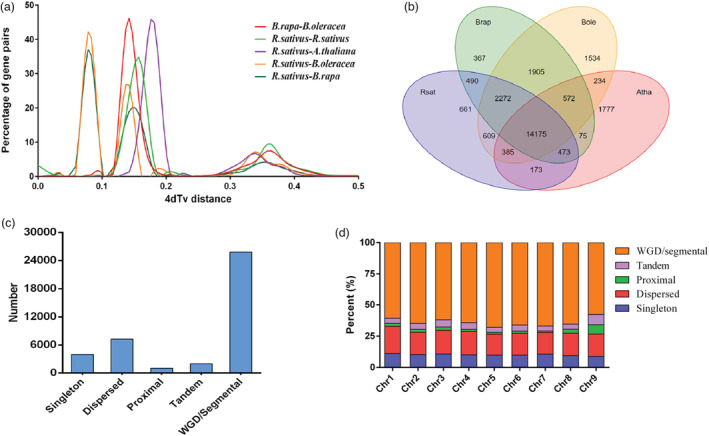
Comparative genomic and genome evolutionary analysis of the radish genome. (a) 4dTv distance distribution of duplicated gene pairs in syntenic blocks within the genomes of Raphanus sativus, Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica rapa and B. oleracea. (b) Venn diagram of shared orthologous gene families among R. sativus, A. thaliana, B. rapa and B. oleracea. (c) Classification of gene duplicates origin in the NAU‐LB genome. The origins of gene duplicates were classified into five types: whole genome/segmental duplication (collinear genes in collinear blocks), tandem duplication (consecutive repeat), proximal duplication (two duplicated genes are distributed adjacent to each other on chromosomes, with no more than 10 genes spaced but not adjacent), dispersed duplication (duplication type other than WGD/segmental, tandem and proximal) and singleton (no duplication). (d) Number of gene duplicates on each chromosome of the NAU‐LB genome.
