Fig. 5.
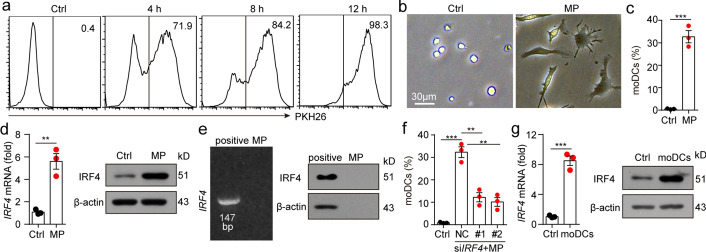
T-MPs induce monocytes to upregulate the expression of IRF4. a PKH26-labeled H22-MPs were co-incubated with BALB/c mouse monocytes for 4, 8, or 12 h, and the engulfment of H22-MPs by monocytes was measured by flow cytometry. b, c Monocytes and H22-MPs were co-incubated for 48 h, and the cell morphology was observed under an inverted microscope (b). The percent of CD11c+MHCII+CD64+ moDCs was measured via flow cytometry (c). d Monocytes were co-incubated with H22-MPs. After 24 or 48 h, RNA or protein were collected respectively. Then, the expression of IRF4 was measured at the levels of both gene and protein. e IRF4 mRNA and protein expression of H22-MPs was measured by RT-PCR and western blot. BALB/c mouse bone marrow-derived monocytes co-incubated with H22-MPs were served as positive controls for H22-MPs. f Monocytes transfected with NC siRNA or IRF4 siRNA were cultured with H22-MPs for 48 h. The percent of CD11c+MHCII+CD64+ moDCs was analyzed by flow cytometry. g BALB/c mice were subjected to H22-MPs or PBS via i.m. injection. 24 or 48 h later, IRF4 expression of isolated monocytes from thigh muscles was analyzed at the levels of both gene and protein. Mean ± s.e.m. is represented in the data and two-tailed unpaired Student's t test was used to statistically analyze the P values. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001